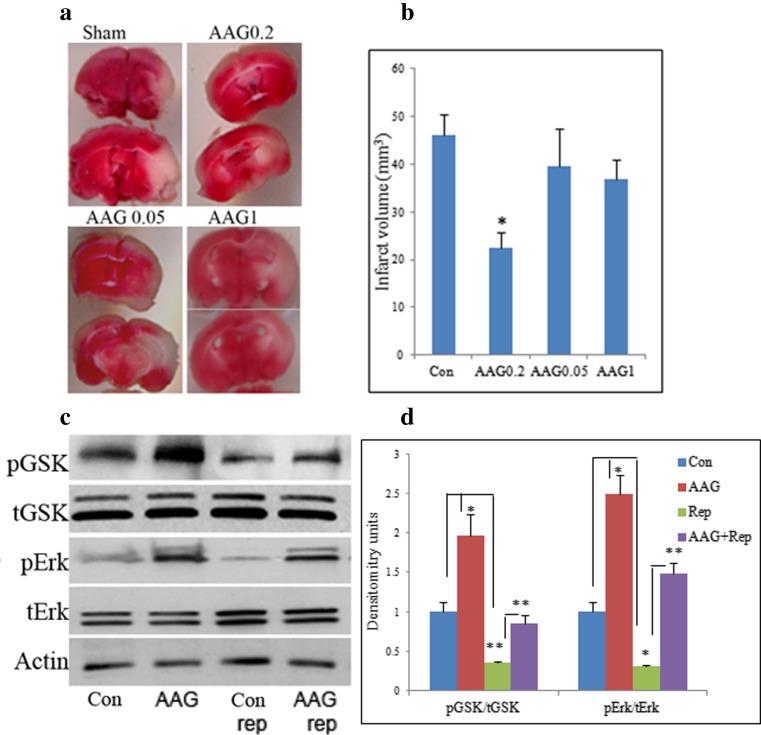
Fig. 4.
17AAG reduces infarct volume in MCAO mouse brains. a: 17AAG reduced infarct size caused by MCAO in a dose-dependent manner. 17AAG of different doses was IP injected into 3 month old male C57Bl/6 mice before introducing MCAO. 17AAG doses were: AAG0.05, 0.05 mg/kg body weight; AAG0.2, 0.02 mg/kg body weight; AAG1, 1 mg/kg body weight. Note 0.2 mg/kg 17AAG significantly reduced the infarct volume, while 0.05 mg/kg and 1 mg/kg had little effects. b: Quantification of the infarct volume with image J. Sample sizes were: Con, N = 9; AAG0.05, N = 7; AAG0.2, N = 11; AAG1, N = 10. c: Western blot analysis of indicated proteins on whole brain lysates of mice injected with 0.2 mg/kg 17AAG. Note 17AAG greatly increased pGSK-3β and pERK levels in brains of mice without MCAO (compare lane 2 to lane 1) as well as those after MCAO (compare lane 4 to lane 3). Actin was used as a loading control. d: Densitometry analysis of the bands shown in C. *, p < 0.05, **, p < 0.01