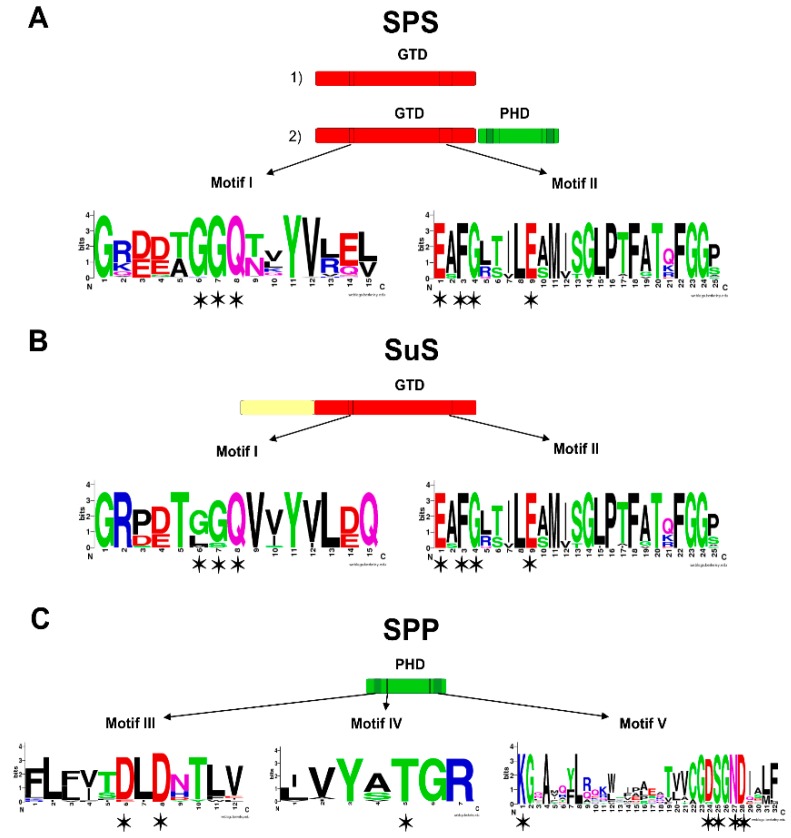
Figure 2.
Domainal arrangements of sucrose-synthesis related proteins. SPS, SPP and SuS (sucrose-synthesis related proteins) are modular proteins based on a glycosyltransferase domain (GTD, red box) and a phosphohydrolase domain (PHD, green box) [9,19]. (A) Two domain arrangements have been described for cyanobacterial SPSs: (1) the minimal SPS unit (GTD), or unidomainal SPS; and (2) the two-domain SPS prototype (GTD-PHD) or bidomainal SPS; (B) SuS presents a GTD, with a characteristic N-terminal extension (yellow box). The resolution of the crystallographic structure of Halothermothrix orenii SPS (2r66A and 2r68A) [24], and of Arabidopsis thaliana SuS1 (3s28A) [25] allowed the identification of the residues involved in the sugar and in the NDP-glucose binding sites, within motif I and II, respectively (denoted with asterisks); (C) SPPs exhibit only a PHD. Motives III to V are characteristic of proteins grouped in the phosphohrydrolase superfamily and related to SPP activity. The crystallization Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 SPP (1s2oA) led to the identification of the residues involved in the catalytic activity [26]. The critical residues were found within PHD motives (denoted with asterisks). Logos were constructed using the above mentioned conserved motives (WebLogo server [27]).