Figure 2.
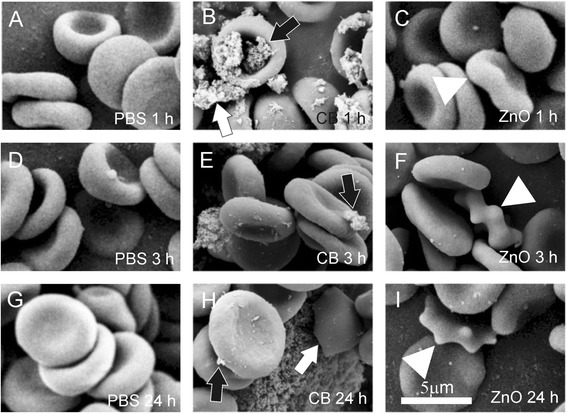
The effect of carbon black nanomaterial on washed human erythrocytes. The effect of carbon black (CB) nanomaterial on washed human erythrocytes as observed by scanning electron microscope. Panels A, D and G show the control samples with added citrated and phosphate buffered saline (PBS); panels B, E and H show the samples with added PBS-suspended CB nanomaterial after 1 hour, 3 hours and 24 hours of incubation, respectively and panels C, F and I show the samples with added PBS-suspended ZnO after 1 hour, 3 hours and 24 hours, respectively. Large CB agglomerates adhered to the erythrocyte surface (B, E, H, black arrows). Agglomerate which adhered to two erythrocytes mediated a bridging interaction between them (B, white arrow). In ZnO-treated samples, singular echinocytes were found (C, F, I, white triangles).
