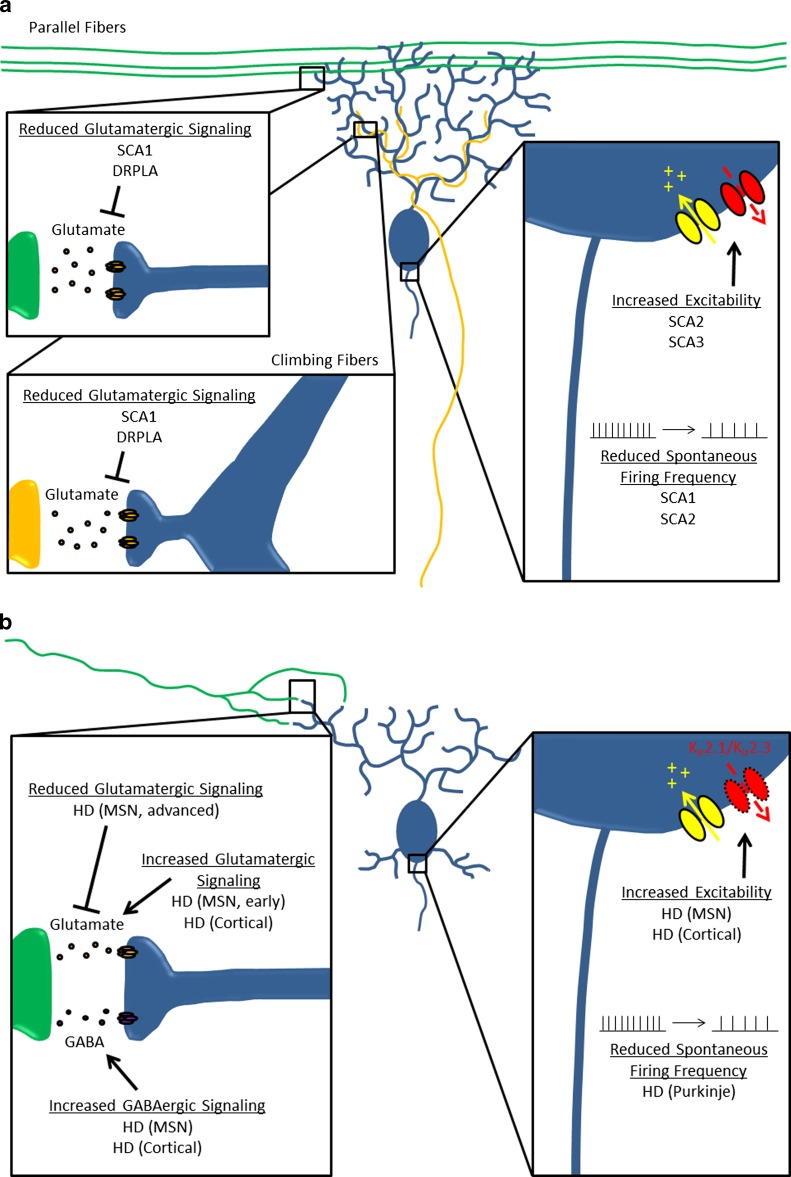
Fig. 1.
Abnormal neuronal activity in polyglutamine (polyQ) disorders. This summarizes the abnormalities in intrinsic excitability and synaptic dysfunction that have been identified in models of polyQ disorders. The inset(s) to the left specifically highlights synaptic dysfunction, while the inset to the right highlights abnormalities of intrinsic excitability. (A) Abnormal Purkinje neuron activity in spinocerebellar ataxia (SCA)1, SCA2, and SCA3, and dentatorubral-pallidoluysian atrophy (DRPLA). (B) Abnormal activity of multiple neuronal subtypes in Huntington disease (HD). MSN = medium spiny neuron; GABA = gamma-aminobutyric acid