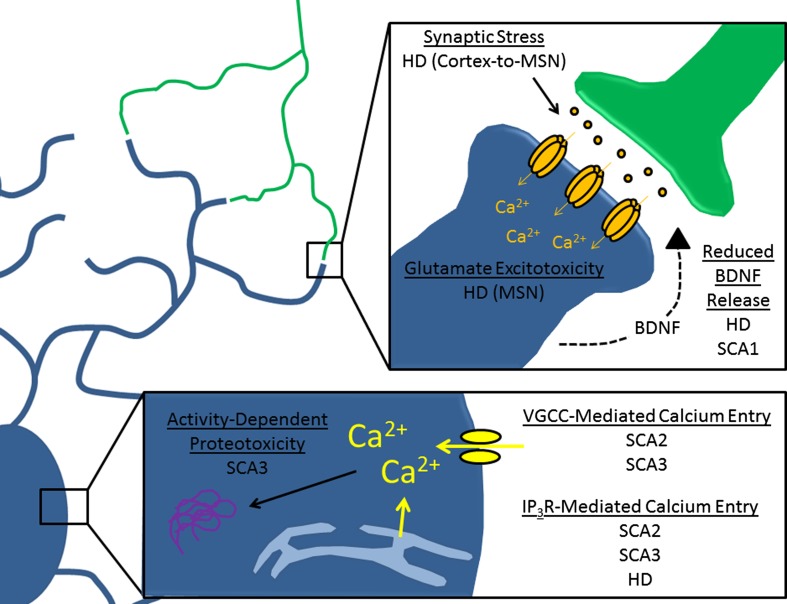
Fig. 2.
Mechanisms of toxicity linked to abnormal neuronal activity in polyglutamine (polyQ) disorders. This diagram highlights mechanisms by which abnormal neuronal activity might produce toxic injury in affected cells. The bottom inset summarizes changes associated with calcium handling, while the top inset summarizes changes associated with synaptic signaling. HD = Huntingdon disease; MSN = medium spiny neuron; BDNF = brain-derived neurotrophic factor; SCA = spinocerebellar ataxia; VGCC = voltage-gated calcium channels; IP3R = inositol-1,4,5 triphosphate receptor