Abstract
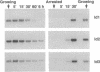
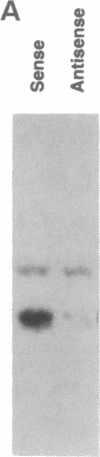
Id1, Id2, and Id3 (HLH462) dimerize with members of the basic helix-loop-helix protein family, but due to the absence of the basic region, the resulting heterodimers cannot bind DNA. Therefore Id-type proteins negatively regulate DNA binding of the basic helix-loop-helix proteins. Here we report that Id1, Id2, and Id3 are induced shortly after serum stimulation in arrested NIH 3T3. Antisense oligonucleotides against the Id mRNAs delay the reentry of arrested cells into the cell cycle elicited by stimulation with serum or growth factors. Antisense oligonucleotides against all three Id mRNAs are more effective than individual ones. Combined, these results indicate that Id proteins are involved in the control of growth induction.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alemá S., Tató F. Interaction of retroviral oncogenes with the differentiation program of myogenic cells. Adv Cancer Res. 1987;49:1–28. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60792-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barone M. V., Henchcliffe C., Baralle F. E., Paolella G. Cell type specific trans-acting factors are involved in alternative splicing of human fibronectin pre-mRNA. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1079–1085. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03476.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benezra R., Davis R. L., Lockshon D., Turner D. L., Weintraub H. The protein Id: a negative regulator of helix-loop-helix DNA binding proteins. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):49–59. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90214-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggs J., Murphy E. V., Israel M. A. A human Id-like helix-loop-helix protein expressed during early development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 15;89(4):1512–1516. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.4.1512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanar M. A., Rutter W. J. Interaction cloning: identification of a helix-loop-helix zipper protein that interacts with c-Fos. Science. 1992 May 15;256(5059):1014–1018. doi: 10.1126/science.1589769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christy B. A., Sanders L. K., Lau L. F., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A., Nathans D. An Id-related helix-loop-helix protein encoded by a growth factor-inducible gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1815–1819. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crescenzi M., Fleming T. P., Lassar A. B., Weintraub H., Aaronson S. A. MyoD induces growth arrest independent of differentiation in normal and transformed cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8442–8446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. L., Cheng P. F., Lassar A. B., Weintraub H. The MyoD DNA binding domain contains a recognition code for muscle-specific gene activation. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):733–746. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90088-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. L., Weintraub H., Lassar A. B. Expression of a single transfected cDNA converts fibroblasts to myoblasts. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):987–1000. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90585-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan M., DiCicco-Bloom E. M., Xiang X., Benezra R., Chada K. The gene for the helix-loop-helix protein, Id, is specifically expressed in neural precursors. Dev Biol. 1992 Nov;154(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(92)90042-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis H. M., Spann D. R., Posakony J. W. extramacrochaetae, a negative regulator of sensory organ development in Drosophila, defines a new class of helix-loop-helix proteins. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):27–38. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90212-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jen Y., Weintraub H., Benezra R. Overexpression of Id protein inhibits the muscle differentiation program: in vivo association of Id with E2A proteins. Genes Dev. 1992 Aug;6(8):1466–1479. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.8.1466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Baltimore D. A new DNA binding and dimerization motif in immunoglobulin enhancer binding, daughterless, MyoD, and myc proteins. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):777–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90682-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Vaessin H., Caudy M., Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N., Cabrera C. V., Buskin J. N., Hauschka S. D., Lassar A. B. Interactions between heterologous helix-loop-helix proteins generate complexes that bind specifically to a common DNA sequence. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):537–544. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90434-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikura K., Murray J. M. Antisense RNA of proto-oncogene c-fos blocks renewed growth of quiescent 3T3 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):639–649. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepperkok R., Lorenz P., Jakobi R., Ansorge W., Pyerin W. Cell growth stimulation by EGF: inhibition through antisense-oligodeoxynucleotides demonstrates important role of casein kinase II. Exp Cell Res. 1991 Dec;197(2):245–253. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(91)90429-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riabowol K. T., Vosatka R. J., Ziff E. B., Lamb N. J., Feramisco J. R. Microinjection of fos-specific antibodies blocks DNA synthesis in fibroblast cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1670–1676. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorrentino V., Pepperkok R., Davis R. L., Ansorge W., Philipson L. Cell proliferation inhibited by MyoD1 independently of myogenic differentiation. Nature. 1990 Jun 28;345(6278):813–815. doi: 10.1038/345813a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun X. H., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A., Baltimore D. Id proteins Id1 and Id2 selectively inhibit DNA binding by one class of helix-loop-helix proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;11(11):5603–5611. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.11.5603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapscott S. J., Davis R. L., Thayer M. J., Cheng P. F., Weintraub H., Lassar A. B. MyoD1: a nuclear phosphoprotein requiring a Myc homology region to convert fibroblasts to myoblasts. Science. 1988 Oct 21;242(4877):405–411. doi: 10.1126/science.3175662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Davis R., Tapscott S., Thayer M., Krause M., Benezra R., Blackwell T. K., Turner D., Rupp R., Hollenberg S. The myoD gene family: nodal point during specification of the muscle cell lineage. Science. 1991 Feb 15;251(4995):761–766. doi: 10.1126/science.1846704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]