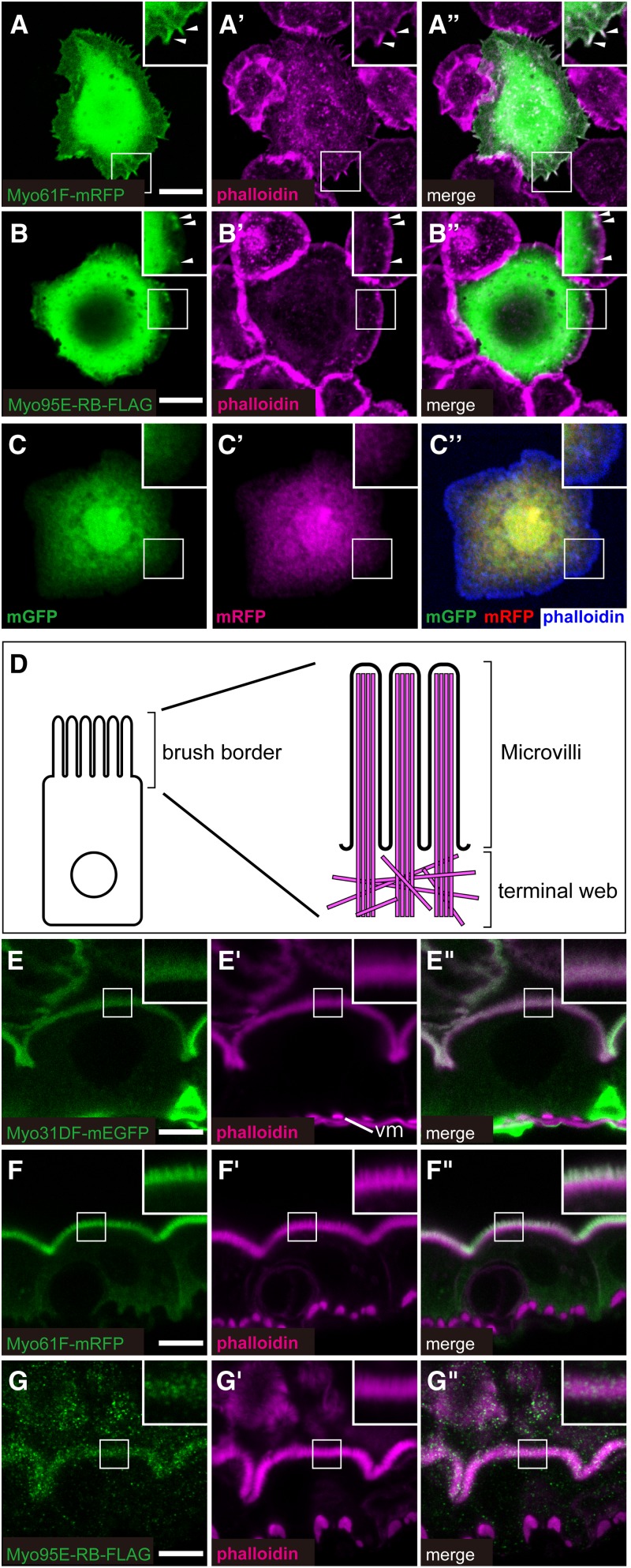
Figure 5.
Subcellular localization of Drosophila class I myosin proteins. (A–C) Subcellular localization of Myo61F-mRFP (green in A and A′′), Myo95E-RB-FLAG (green in B and B′′), and control proteins mGFP (green in C and C′′) and mRFP (magenta in C′ and C′′) in Drosophila S2 cells. F-actin (magenta in A′, A′′, B′, and B′′ and blue in C′′) was stained by fluorescently labeled phalloidin. Insets in A–C′′ are high magnifications of the areas shown by white squares, and arrowheads in the insets (A–B′′) indicate the colocalization of Myo61F-mRFP or Myo95E-RB-FLAG with F-actin. A′′, B′′, and C′′ are merged images of A and A′, B and B′, and C and C′, respectively. (D) Schematic diagram of an enterocyte (left) and its brush border F-actin structure (right, magenta), showing the microvilli and terminal web. (E–G′′) Subcellular localization of Myo31DF-mEGFP (green in E and E′′), Myo61F-mRFP (green in F and F′′), and Myo95E-RB-FLAG (green in G and G′′), which were overexpressed in the larval midgut enterocytes. The F-actin-enriched apical domain was stained by fluorescently labeled phalloidin (magenta in E′, E′′, F′, F′′, G′, and G′′). Insets in E–G′′ are high magnifications of the areas shown by white squares. In E′, vm indicates visceral muscle. E′′, F′′, and G′′ are merged images of E and E′, F and F′, and G and G′, respectively. Bars, 10 μm.