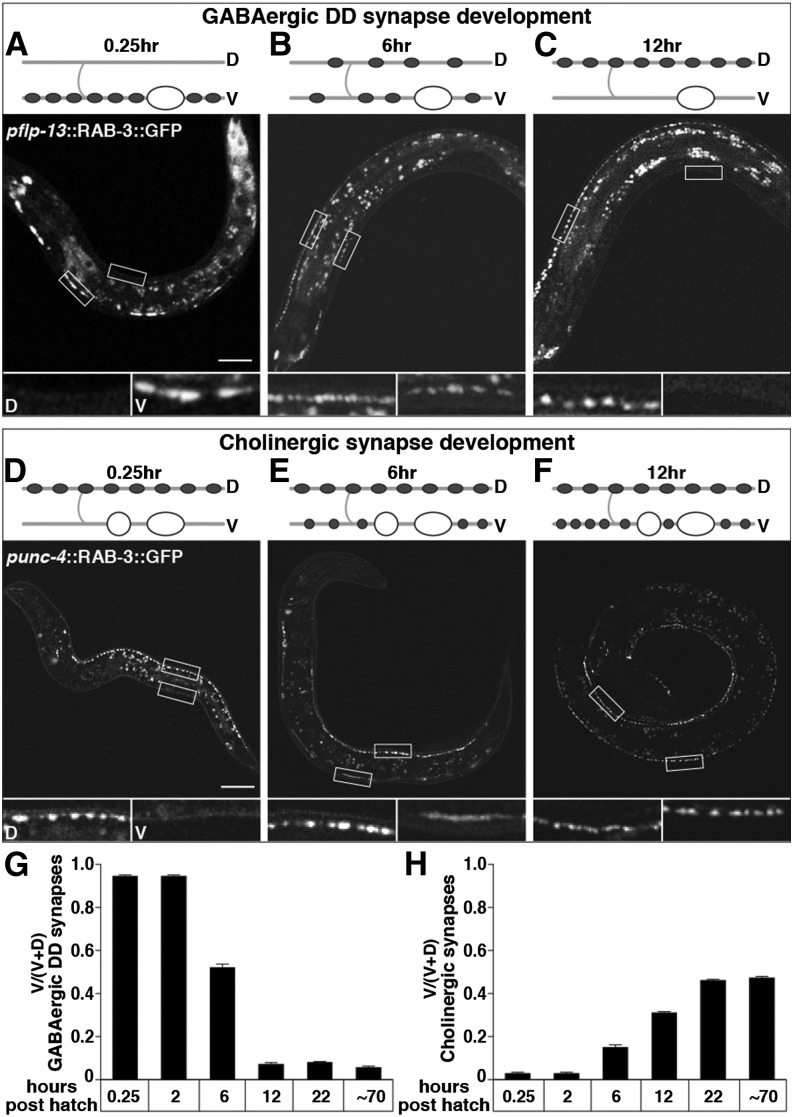
Figure 5.
Presynaptic motor neuron development coincides with the postsynaptic switch in muscle response to muscimol. (A–C) Rewiring of DD presynaptic termini from ventral to dorsal in L1 animals. Wild-type animals expressing GFP::RAB-3 in GABAergic DD motor neuron presynaptic termini under the flp-13 promoter at 0.25 (A), 6 (B), and 12 (C) hr posthatch. (D–F) Development of ventral cholinergic presynaptic termini in L1 animals. Wild-type animals expressing GFP::RAB-3 in cholinergic motor neuron presynaptic termini under the unc-4 promoter at 0.25 (D), 6 (E), and 12 (F) hr posthatch. Cartoons depict a representative DD motor neuron (A–C) or ventral cholinergic motor neuron (D–F) and where their synapses are at each time point. Shaded lines, nerve cords and commissures; “D” and “V”, dorsal, ventral; open ovals, DD motor neuron cell bodies; solid ovals, synapses made from DDs; open circles, ventral cholinergic motor neuron cell bodies; solid circles, synapses made from ventral cholinergic motor neurons. All animals are oriented with head to the left and ventral down. Open boxes outline representative regions of the dorsal and ventral nerve cord that are shown in magnified versions below each image and labeled “D” and “V” for dorsal and ventral in A and D. Magnified images in B, C, E, and F similarly show the dorsal box on the left and the ventral box on the right. Bar, 20 µm. (G and H) Quantification of the proportion of ventral GFP::RAB-3 in DD presynaptic termini (G) or in cholinergic presynaptic termini (H). n = 20 animals.