Figure 1.
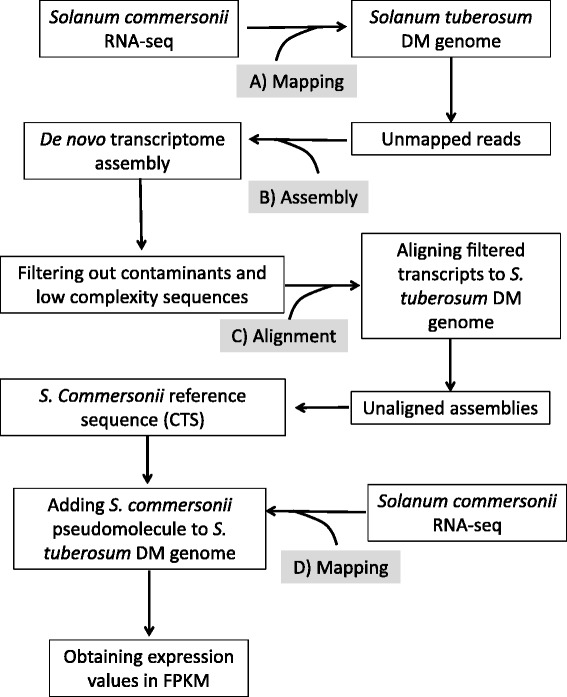
Workflow of analysis of root RNA samples from the S. commersonii accessions and generation of the S. commersonii reference sequence. A) RNA-seq reads were mapped using TopHat [37] to Solanum tuberosum DM genome and unmapped reads were retained. B) Unmapped reads were filtered for low quality and artifacts using Cutadapt and FASTX toolkit [71,72]. The cleaned reads were used to carry out a de novo transcriptome assembly using Oases [38]. The assembled transcripts were filtered out for low complexity sequences and possible contamination by searching sequences against the Uniref100 database. C) High quality transcripts assemblies were aligned to S. tuberosum DM genome using Gmap [42] and unaligned transcripts were kept for further analyses. In order to eliminate redundancy only the longest isoform from each Oases locus was used as the representative transcript. Representative transcripts were used to create a reference sequence that was added as an additional chromosome to the S. tuberosum DM genome. D) Solanum commersonii RNA-seq was mapped to the S. tuberosum DM genome and S. commersonii lineage specific concatenated transcript sequences using TopHat. After mapping, expression values were obtained using Cufflinks [43].
