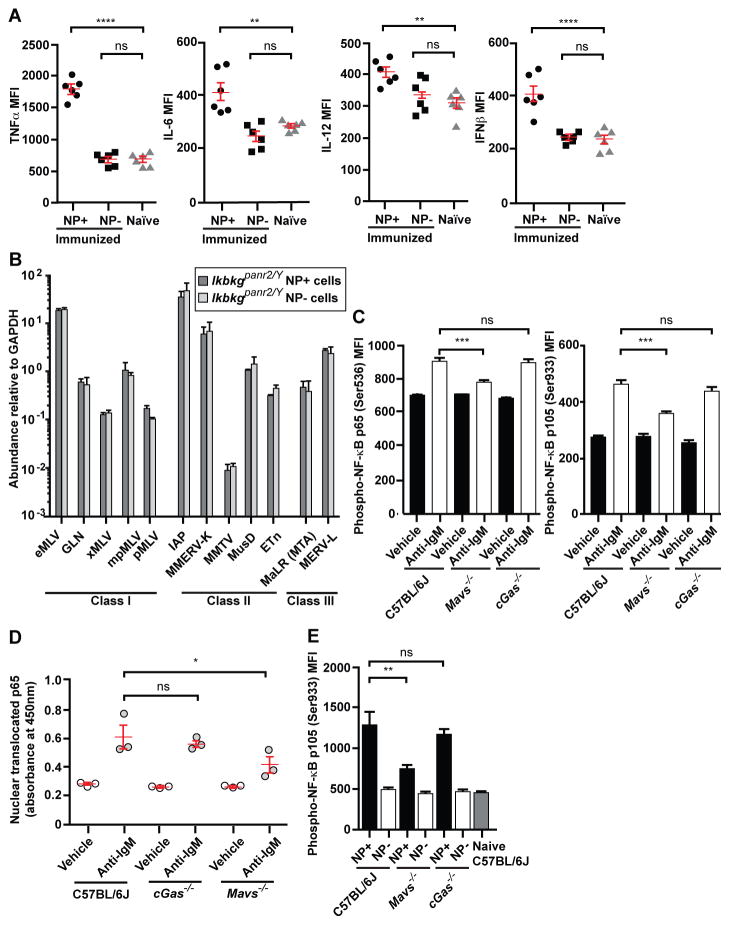
Figure 5. NF-κB is required for ERV induction and is activated by BCR and MAVS signaling.
(A, B) Splenic NP-specific or non-NP-specific CD19+ B cells were collected from mice 4.5 days post-immunization with NP-Ficoll. (A) Cytokine expression in the indicated B cells from C57BL/6J mice. (B) Transcript levels of the indicated ERVs measured by RT-qPCR of mRNA isolated from NP-specific or non-NP-specific B cells. N = 3 mice. No significant difference was found between NP+ and NP− cells for any ERV tested. (C–D) Splenic B cells were cultured in vitro and stimulated with anti-IgM or vehicle for 22 hr. (C) Levels of phospho-p65 (left) and phospho-p105 (right). N = 3 mice. (D) Levels of p65 in the nuclear fraction of cells. (E) Levels of phospho-p105 in splenic NP-specific and non-NP-specific CD19+ B cells or naïve B cells on day 6 post-NP-Ficoll immunization. N = 3 mice per genotype. MFI, mean fluorescence intensity. Data points represent individual mice (A, D). P values were determined by Student’s t test (B) or one-way ANOVA and post hoc Tukey test (A, C–E). Results are representative of 2 independent experiments.