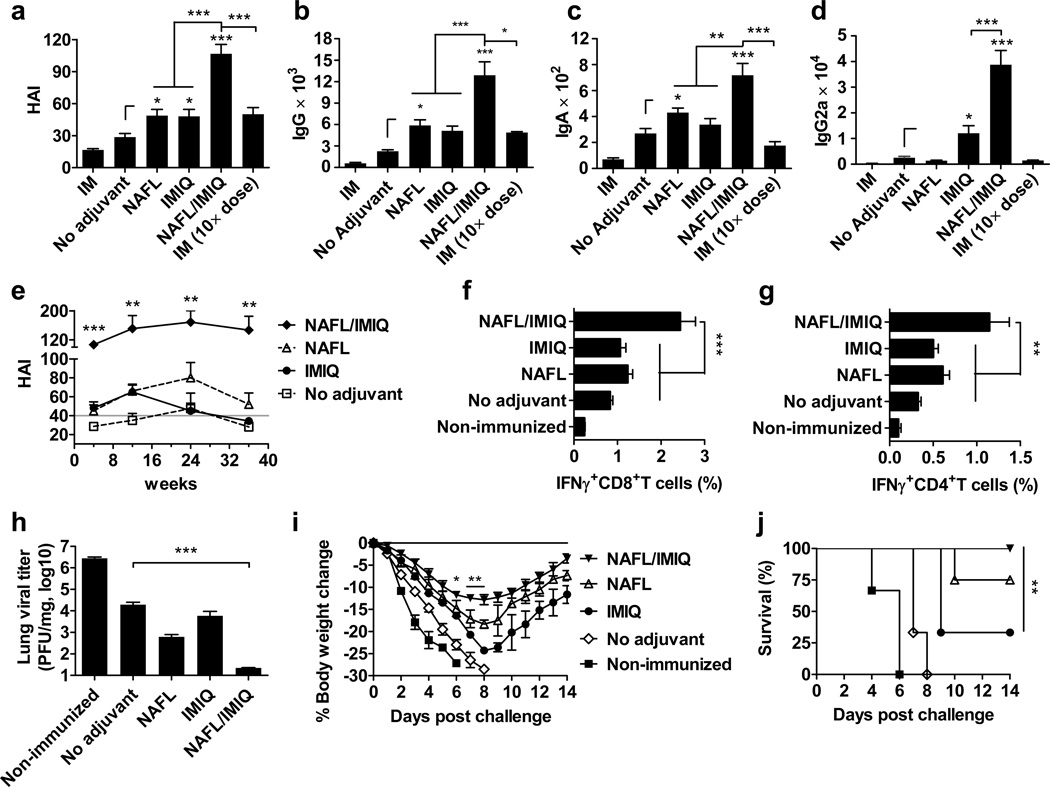
Figure 1. NAFL/IMIQ strengthens immunogenicity of ID influenza vaccine.
BALB/c mice were ID immunized with 0.06 µg (HA content) H1N1 influenza vaccine alone (no adjuvant) or in the presence of NAFL, IMIQ, or NAFL/IMIQ adjuvant or IM immunized with a same dose (IM) or a 10× higher dose (0.6 µg) of the vaccine. Humoral immune responses were measured 4 weeks later including HAI titer (a), IgG (b), IgA (c) or IgG2a (d). HAI titers were further monitored at 4, 12, 24, and 36 weeks post immunization (e). A horizontal gray line indicates a standard protective titer of HAI. n=8, except for NAFL and NAFL/IMIQ groups (n=10). (f, g) Cell-mediated immune responses. PBMCs were isolated one week after immunization, stimulated with the vaccine and anti-CD28 antibody and analyzed for the percentages of IFNγ-secreting CD8+ (f) and CD4+ (g) T cells by flow cytometry. n=6, except for NAFL and NAFL/IMIQ groups (n=8). (h-j) Challenge studies. The immunized mice and non-immunized controls were intranasally challenged with 10× LD50 of A/California/7/2009 H1N1 virus 5 weeks post-immunization. The infected mice were euthanized 4 days post-infection to determine lung viral titers by TCID50 assays using MDCK cells (h). n=6. Body weight (i) and survival (j) were monitored daily for 14 days. Percentages of body weight dropped relative to a pre-infection level and percentages of survivals were compared between NAFL/IMIQ and NAFL or IMIQ groups by t-test or Logrank test respectively. n=6, except for NAFL and NAFL/IMIQ groups (n=8). Data are presented as mean ± s.e.m. Statistical significance was analyzed by ANOVA/Bonferroni unless noted otherwise. *, p<0.05; **, p< 0.01 or ***, p<0.001, respectively. All experiments were repeated twice with similar results.