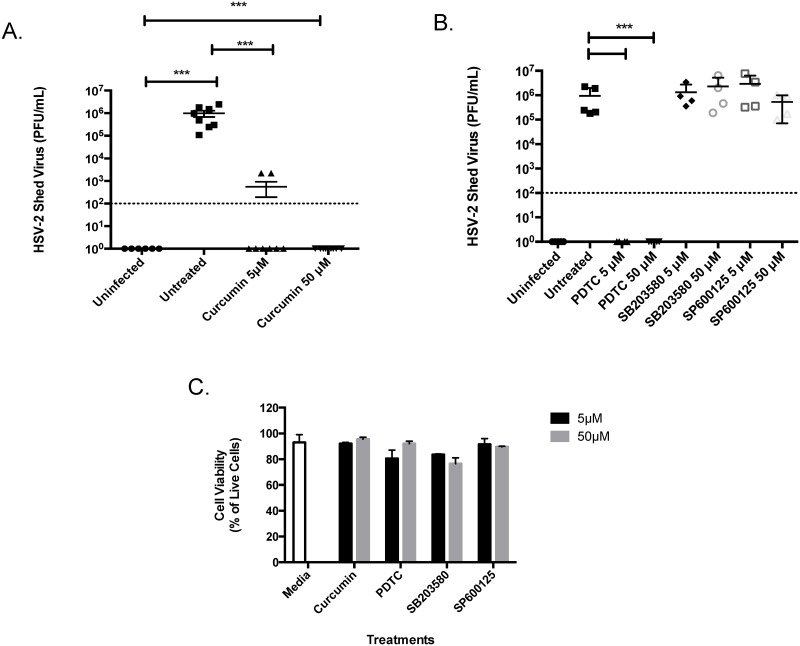
Fig 6. Inhibition of inflammatory signalling pathways decreases HSV-2 viral shedding.
Primary GECs were grown to confluency and were pre-treated with media (untreated) or 5 or 50 μM of curcumin (A) or PDTC the NFκB inhibitor, SB203580 a p38 MAP kinsase inhibitor or SP600125 an inhibitor of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) (B) for 1 hour. The cells were then exposed to 104 PFU of HSV-2 strain 333 for 2 hours. At 24-hours post-infection, apical cell culture supernatants were collected and the amount of shed HSV-2 was measured using a standard Vero plaque assay. To assess whether the inhibitors used in this study affected cell viability (C), primary GECs were exposed to media control, or curcumin, PDTC, SB203580 or SP600125 at 5 or 50 μM for 1 hour. Following exposure, cells were collected and cell viability was calculated using the trypan exclusion assay. Results are reported as the percent of live cells in culture. Data shown represents the mean ± SEM of three separate experiments. A minimum of two replicates per experimental condition was included in every experiment performed. Data analyzed using the Kruskal-Wallis non-parametric analysis of variance with Dunn’s test to correct for multiple comparisons. ***p<0.001. HSV-2: herpes simplex virus type 2; PFU: plaque-forming units; PDTC: pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate.