Figure 7.
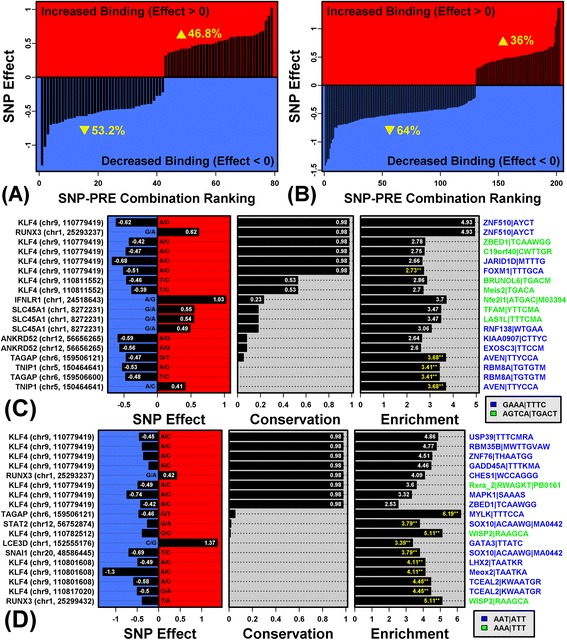
Identification of enhancer-associated non-coding psoriasis susceptibility loci as potential sites of allele-specific transcription factor binding. We examined 53 psoriasis-associated non-coding SNPs within an NHEK enhancer to identify SNP-PRE combinations representing possible sites of allele-specific TF binding. (A) Predicted effects of risk alleles with respect to 79 SNP-PRE combinations involving PRE motifs enriched in sequences upstream of PP-increased DEGs (FDR < 0.10) (see Methods, Equation 3). (B) Predicted effects of risk alleles with respect to 203 SNP-PRE combinations involving PRE motifs enriched in sequences upstream of PP-decreased DEGs (FDR < 0.10). (C) The 79 SNP-PRE combinations from (A) were filtered to identify those for which the SNP locus is conserved and/or the PRE is recognized by a PP-increased DEG. (D) The 203 SNP-PRE combinations from (B) were filtered to identify those for which the SNP locus is conserved and/or the PRE is recognized by a PP-decreased DEG. In both (C) and (D), we list the SNP’s genomic location and nearest gene (left margin) and the PRE motif label for the corresponding PWM matrix (right margin). The phastcons conservation score for the SNP locus is also shown, along with Z statistic indicating how strongly the PWM motif was enriched in sequences upstream of (C) PP-increased DEGs or (D) PP-decreased DEGs. The Z statistic is listed within the bar graphs, with yellow text denoting cases in which the PWM is recognized by (C) a PP-increased DEG or (D) a PP-decreased DEG.
