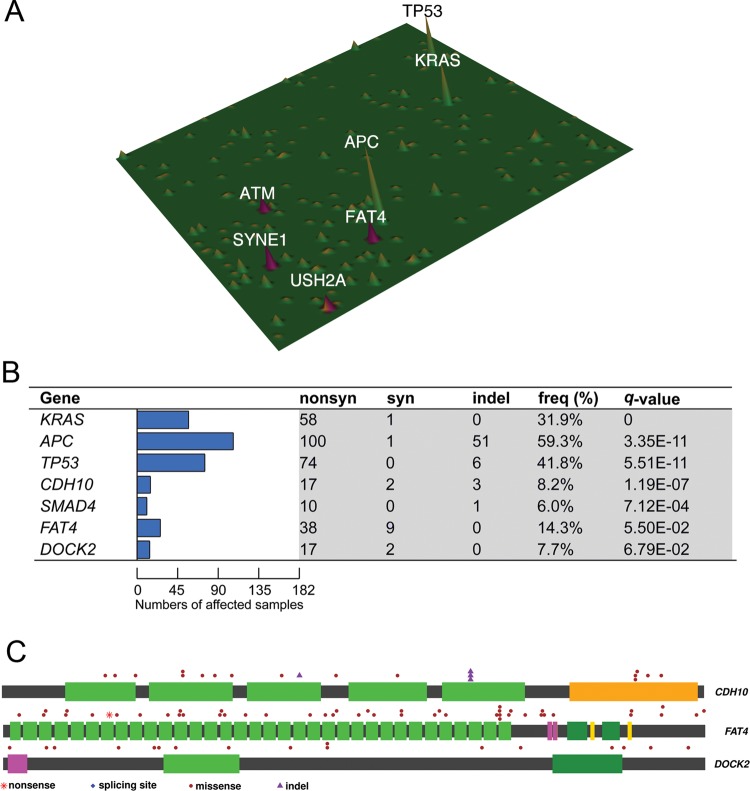
Figure 3.
Identification of novel high-frequency and significantly mutated genes by targeted capture sequencing in CRC. (A) Mutation landscape of 160 capture-sequenced patients with CRC was depicted in which several novel mutated genes (ie, SYNE1, FAT4, ATM, USH2A) were shown to exhibit mutation frequency of ≥10%. (B) Significantly mutated genes (SMGs) in which non-silent mutations were positively selected over silent mutations were identified in 182 exome-sequenced and capture-sequenced patients with CRC and ranked by q-value. Such analysis reaffirmed APC, KRAS, TP53 and SMAD4 mutations as major driver events in CRC. Our analysis also revealed three novel SMGs, namely FAT4, CDH10 and DOCK2, previously undescribed in CRC. (C) Distribution of somatic mutations in the three newly identified SMGs was shown.