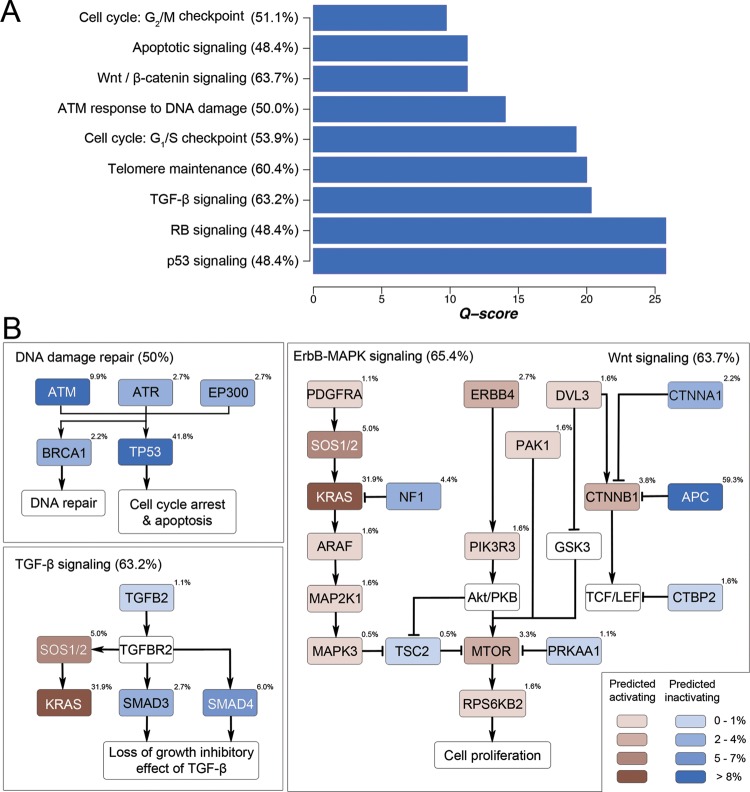
Figure 4.
Signalling pathways genetically altered in CRC. (A) Significantly mutated pathways with positive selection of non-silent mutations were ranked by Q-score. (B) Mutation frequencies of individual signalling components of four major signalling pathways, namely, Wnt signalling, ErbB signalling, transforming growth factor-β signalling and DNA damage sensing/repair, in 182 patients with CRC were shown. These pathways exhibited genetic alteration in a majority (50–65%) of CRC samples.