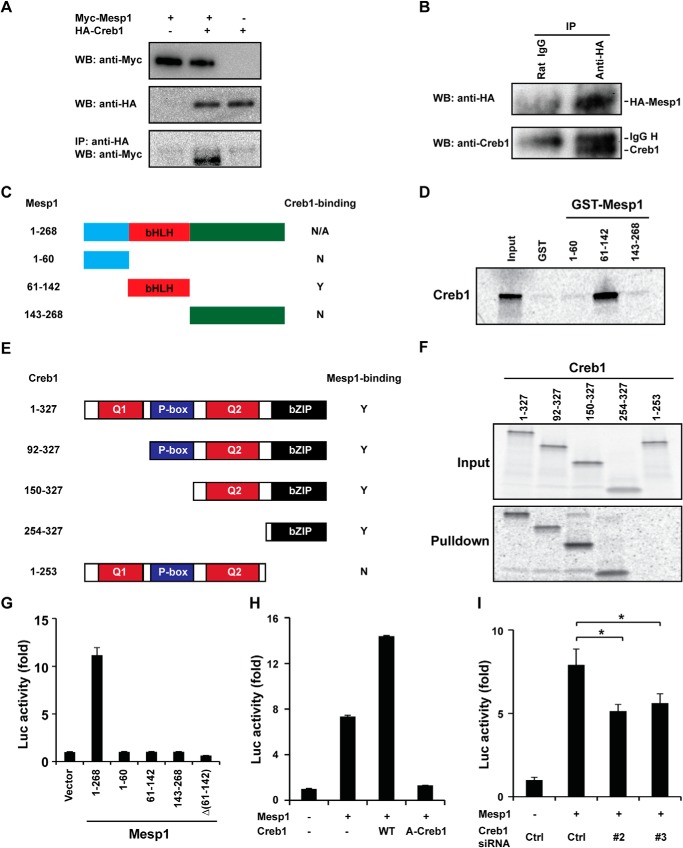
FIGURE 3.
Mesp1 interacts directly with Creb1. A, Myc-Mesp1 and HA-Creb1 are overexpressed in C2C12 cells. Overexpression of Myc-Mesp1 and HA-Creb1 is detected using Western blot analysis and anti-Myc or anti-HA sera, respectively. Myc-Mesp1 is coimmunoprecipitated (IP) with HA-Creb1 using a HA antibody (Western blot (WB), anti-Myc). B, HA-Mesp1 is overexpressed to a similar level of endogenous Mesp1 in EBs on day 4. HA-Mesp1 is immunoprecipitated successfully by anti-HA (top panel). Endogenous Creb1 is detected using an anti-Creb serum (bottom panel). C, the deletional constructs of Mesp1. N, no; Y, yes; N/A, not available. D, 35S-labeled Creb1 is pulled down by GST-Mesp1 (61–142) but not Mesp1 (1–60) or Mesp1 (143–268), as summarized in C. E, the Creb1 deletional construct. Q1 and Q2, Glu-rich domains 1 and 2; P-box, phosphorylation domain. F, deletional Creb1 constructs were translated in vitro in the presence of [35S]methione (Input) and then utilized for a pulldown assay with GST-Mesp1 (61–142). All of the deletions harboring the bZIP domain can be pulled down, whereas the constructs lacking the bZIP domain cannot be pulled down, as summarized in E. G, transcriptional activity of Mesp1 deletions. Full-length Mesp1 transactivates the Etv2 reporter, whereas each domain of Mesp1 or deletion of bHLH domain Δ(61–142) does not transactivate the Etv2 reporter. H, wild-type Creb1 augments the activity of Mesp1. The dominant negative inhibitor A-Creb1 represses the activity of Mesp1 to the baseline level. WT, wild-type Creb1. I, knockdown of Creb1 by siRNA #2 and #3 reduces the activity of Mesp1. Ctrl, control, referring to the RNA-induced silencing complex-free siRNA (*, p < 0.05).