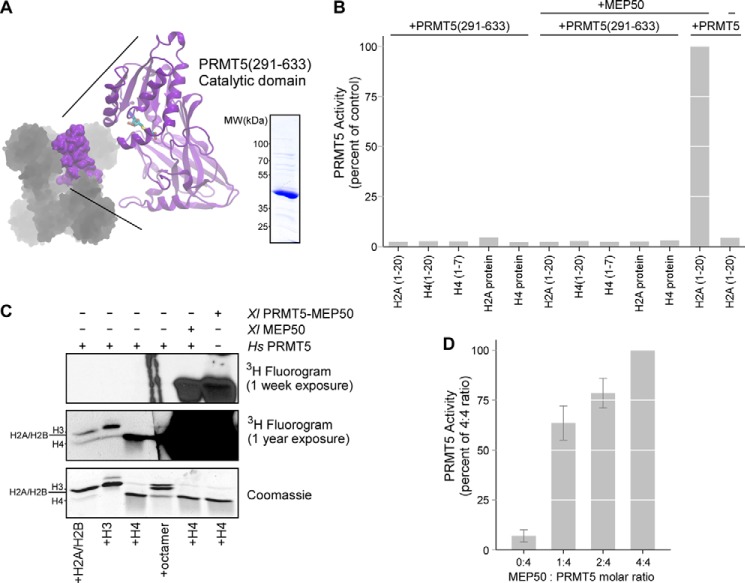
FIGURE 2.
Intact full-length PRMT5 complexed with MEP50 is necessary for histone methyltransferase activity. A, the catalytic C-terminal domain of XlPRMT5 (residues 291–633) is shown in purple and was expressed and purified. B, XlPRMT5(291–633) did not exhibit any activity toward histone tail peptide substrates of the intact complex (H2A(1–20), H4(1–20), H4(1–7)) or full-length histones H2A or H4. The addition of XlMEP50 to the catalytic domain did not stimulate activity, whereas the addition of XlMEP50 to full-length HsPRMT5 stimulated activity toward H2A(1–20) peptide. C, intact XlPRMT5-MEP50 complex or HsPRMT5 + XlMEP50 exhibited methyltransferase activity toward histone H4 (right two lanes). HsPRMT5 alone exhibited ultralow levels of activity toward H2A, H3, and H4, visible only after a 1-year exposure of the fluorogram (left four lanes, second panel). D, HsPRMT5 (200 nm) was preincubated with substoichiometric (1:4 and 2:4) and stoichiometric concentrations (4:4) of XlMEP50 and then assayed for methyltransferase activity against H4 peptide.