Figure 4. Isolation-induced ultrasonic vocalizations.
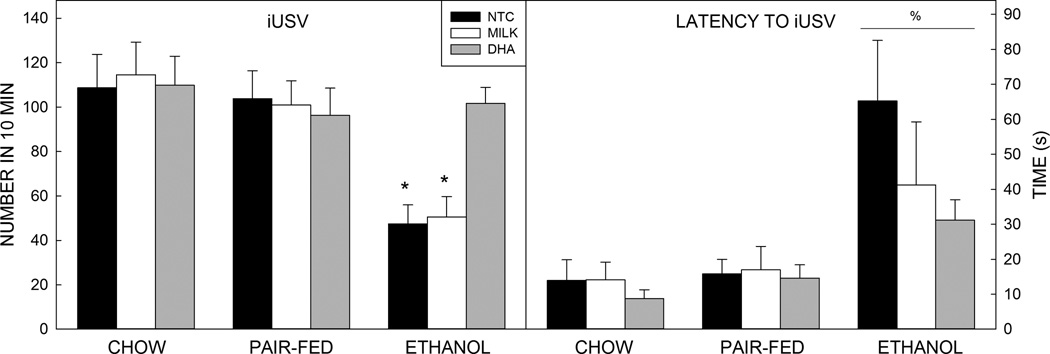
Prenatal exposure to ethanol increased the time until the first vocalization (latency) and the number of vocalizations. Within the ethanol-exposed group, treatment with DHA increased the number of vocalizations but did not alter latency to call.
Data are mean of 10–14 animals per group. T–bars are the standard error of the mean. *significantly (p<0.05) different to Ch (all), PF (all), and Et-DHA. % significantly (p<0.05) different to Ch (all) and PF (all).
