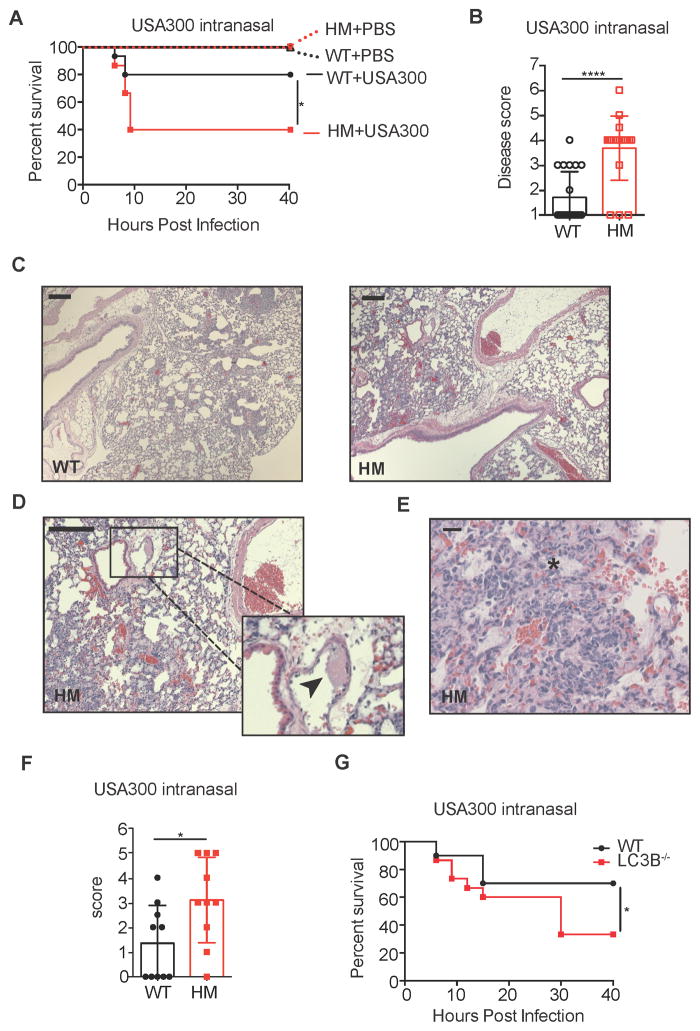
Figure 3. Autophagy Mediates Susceptibility to S. aureus Lung Infection.
(A) Survival curve of WT and Atg16L1HM mice inoculated intranasally with 4x108 cfu USA300 or equivalent volume of PBS. n=15 mice/group for USA300 and n=5 mice/group for PBS.
(B) Disease score of WT and Atg16L1HM mice 6 hours post intranasal inoculation with 4x108 cfu USA300. Disease score was calculated using a 7-point activity assessment score based on mobility, food and water intake, posture, and fur ruffling (see supplemental methods). n=10 mice/group. Data represent mean and SEM.
(C) Representative H&E-stained sections of lungs from WT and Atg16L1HM mice 6 hr post intranasal inoculation with 4x108 cfu USA300. scale bar = 200 μm.
(D–E) Higher magnification images showing features only present in the lungs from Atg16L1HM mice. Black arrow head in (D) indicates fibrin thrombus and asterisk in (E) indicates edema. scale bar = 200 μm (D) or 20 μm (E).
(F) Blind quantification of pathology observed in lungs from WT and Atg16L1HM mice. Score was calculated using a 5-point score based on tissue destruction, hemorrhage, and visible cocci (see supplemental methods). n=10 mice/group. Data represent mean and SEM.
(G) Survival curve of WT and LC3B−/− mice inoculated intranasally with 4x108 cfu USA300. n=15–20 mice/group.
Data represent at least 2 independent experiments. *p<0.05, ****p<0.0001