Figure 2.
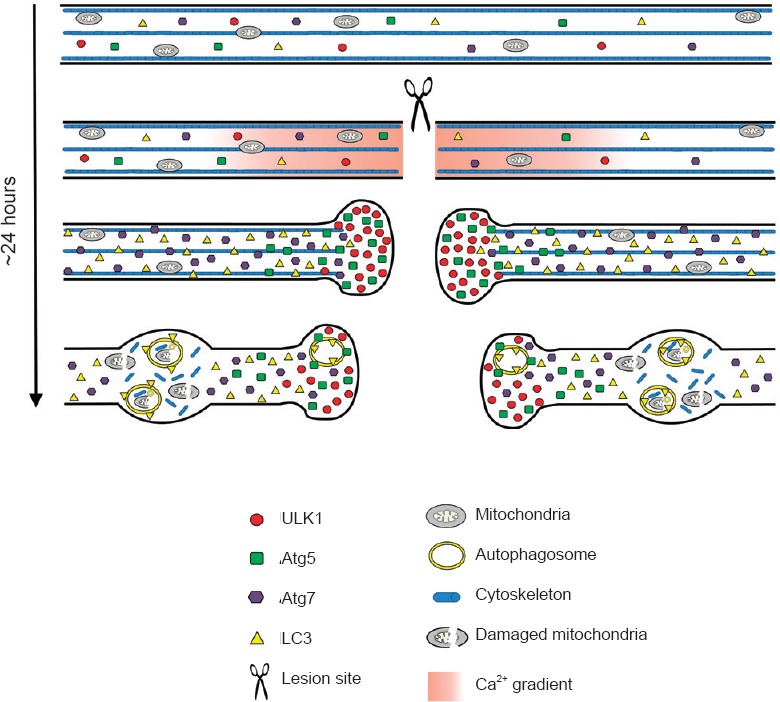
Scheme of the proposed morphological events that occurs in damaged axons after spinal cord injury.
Before lesion, the basal axonal levels of the autophagy-related proteins ULK1, Atg7, Atg5 and LC3 are very low. Injury to the axons of the spinal cord induces a rapid influx of calcium that could activate the autophagy cascade through ULK1 stimulation, which strongly accumulates in the retraction bulbs. Atg5 also accumulates in the retraction bulbs showing puncta-like structures, indicating the presence of phagophores. The accumulation of ULK1 and Atg5 in retraction bulbs suggests that autophagosome biogenesis may take place in this region after the lesion. The Atg7 protein shows an increased expression throughout the damaged axons and could contribute to the spatial propagation of the autophagy cascade. Finally, the diffuse increase of LC3-positive autophagosome suggests that they may be transported through the axons and accumulate in axonal swellings on both sides, rostral and caudal, to the lesion site. Reproduced with permission from Brain Pathology, 2014, doi:10.1111/bpa.12170.
