Figure 3.
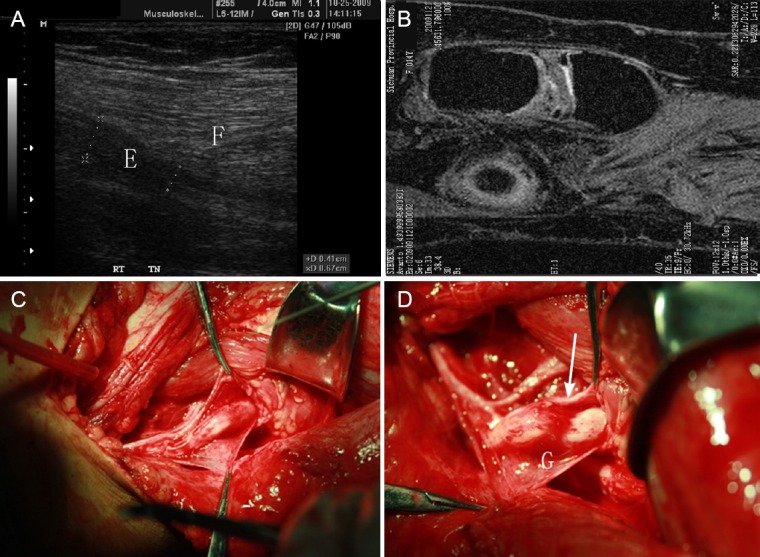
Proximal tibial nerve of one patient with earthquake-caused nerve injury.
(A) Ultrasound image of the proximal tibial nerve of one patient with earthquake-caused nerve injury. A well-localized indentation is shown in the tibial nerve (E) directly beneath the fibromuscular soleal sling (F). (B) MRI image of the fibromuscular soleal sling and tibial nerve. (C) Surgery of the nerve. Proximal is to the left and distal is to the right. The curved line highlights the fibromuscular soleal sling. (D) Same patient with the tibial nerve injury underwent neurolysis and fibromuscular sling retraction (G: Location of compression on the tibial nerve by the fibromuscular sling). Arrow points to the discrete, well-localized indentation in the tibial nerve beneath the fibromuscular soleal sling, which is suggestive of pathologic compression of the tibial nerve.
