Figure 4.
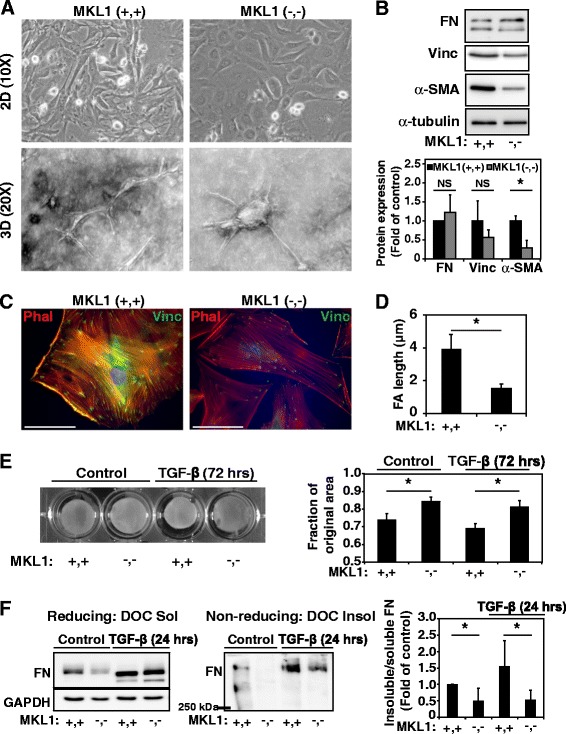
MKL1 is required for contractile functions of the myofibroblast. A. Phase contrast microscopy of representative MKL1 (+,+) and MKL1 (−,-) primary mouse lung fibroblasts (MLF) grown on 2D plates (top row) and 3D in collagen (bottom row) to show morphological differences. B. MKL1 (+,+) and MKL1 (−,-) primary MLF lysates were analyzed by Western blot with antibodies against fibronectin (FN), vinculin, α-SMA and α-tubulin. Densitometry of n = 3 experiments (bottom panel). C. Merged images of 2D primary MLF subjected to immunofluorescent staining with phalloidin rhodamine (red) and or primary antibodies directed against vinculin and FITC-conjugated secondary antibodies (green). D. Cells stained by indirect immunofluorescence against vinculin were analyzed for focal adhesion size by quantitation of vinculin plaque length using ImageJ (as described in methods). E. MKL1 (+,+) and MKL1 (−,-) primary MLF were treated with 1 ng/ml TGF-β (72 hrs) or vehicle control prior to plating into 3D collagen gels for gel contraction assessment over 2 days. Gel areas were quantified from the digital images using ImageJ (right panel). F. MKL1 (+,+) and MKL1 (−,-) MLF were plated, serum-starved and stimulated with 1 ng/ml TGF-β or vehicle control for 24 hours. Cells were subjected to deoxycholate (DOC) extraction, with DOC-soluble and DOC-insoluble lysates subjected to gel electrophoresis under reducing (first panel) and non-reducing (second panel) conditions followed by Western blotting for total fibronectin. Fibronectin bands from both soluble and insoluble lysates were quantified by densitometry and values expressed as the ratio of insoluble to soluble fibronectin (third panel). One-way ANOVA (p < 0.05) was performed to test for statistical significance.
