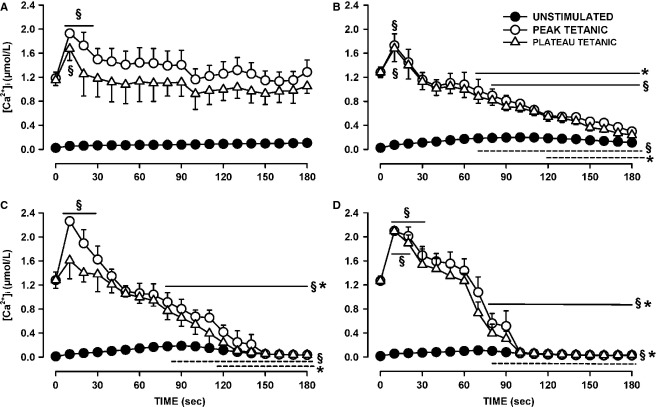
Figure 5.
Changes in unstimulated, peak, and plateau tetanic [Ca2+]i during fatigue between wild-type fibers exposed to 10 μmol/L glibenclamide. Fibers were separated into four groups. (A) fibers for which at the end of fatigue plateau tetanic [Ca2+]i either had increased or decreased by <0.22 μmol/L (n = 4); (B) fibers for which decreases in plateau tetanic [Ca2+]i exceeded 0.5 μmol/L but released Ca2+ upon stimulation throughout the entire fatigue period (n = 7); (C) fibers with decreases in plateau tetanic [Ca2+]i exceeding 0.5 μmol/L and suddenly failed to release Ca2+ between the 120th and 150th sec (n = 3) or (D) between the 90th and 100th sec (n = 5). A lack of Ca2+ release can be seen when there is no difference between unstimulated and tetanic [Ca2+]i. See Figure8 for a better resolution in unstimulated [Ca2+]i between fiber groups. §Mean peak (solid line) or plateau (dashed line) tetanic [Ca2+]i was significantly different from the prefatigue mean value (Time 0 sec). *Mean peak or plateau tetanic [Ca2+]i was significantly different from the mean for the fibers in A, ANOVA and L.S.D. P < 0.05.