Figure 7.
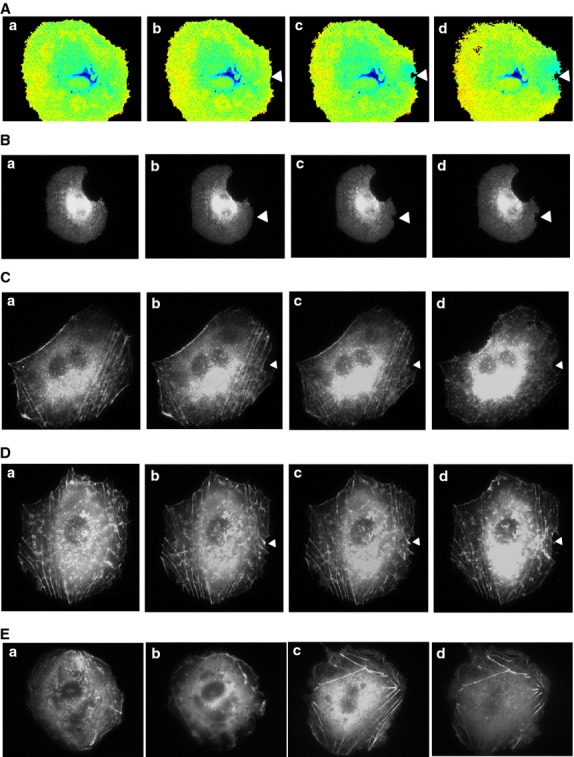
Effect of Gadolinium on TRPV2. (A) Effect of Gadolinium on [Ca2+]s. Focal mechanical stress was applied to the site indicated by the arrow head in the presence of 10 μmol/L gadolinium and changes in the [Ca2+]s were monitored using pm-Cameleon-nano. The results are the representative of four experiments. a: before the application, b: 1 min, c: 3 min, d: 5 min after the application. (B) Effect of Gadolinium on the localization of TRPV2. Focal mechanical stress was applied as indicated by the arrow in the presence of 10 μmol/L gadolinium. Changes in the localization of GFP-TRPV2 were monitored. The results are the representative of four experiments. a: before the application, b: 1 min, c: 3 min, d: 5 min after the application. (C) Effect of focal application of mechanical stress on actin filament. Focal mechanical stress was applied as indicated by the arrowhead and changes in actin filaments were monitored. The results are the representative of four experiments. a: before the application, b: 3 min, c: 5 min, d: 10 min after the application. (D) Effect of Gadolinium of actin filaments. Focal mechanical stress was applied in the presence of 10 μmol/L gadolinium and changes in the actin filaments were monitored. The results are the representative of four experiments. a: before the application, b: 3 min, c: 5 min, d: 10 min after the application. (E) Effect of Gadolinium on EGF-induced changes in actin filaments in the absence of extracellular calcium. Cells were incubated in medium containing no calcium and stimulated with 10 nmol/L EGF (b, d) in the presence (c, d) and absence (a, b) of 10 μmol/L gadolinium and actin filaments were monitored. The results are the representative of two experiments. a, c: before stimulation, b, d: 10 min after the addition of EGF.
