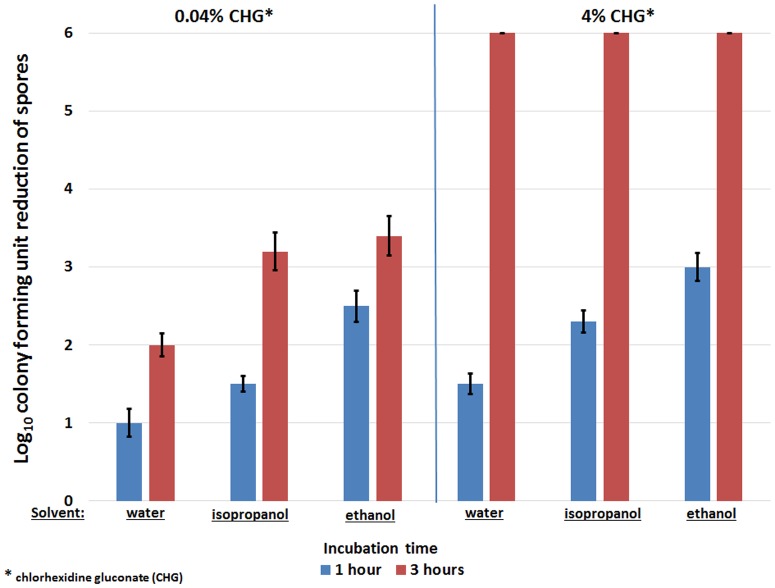
Fig 3. Comparison of heat killing of Clostridium difficile spores in chlorhexidine gluconate (CHG) solutions prepared with isopropanol or ethanol.
The mean log10colony-forming unit (CFU) reductions of C. difficile spores achieved after 1 or 3 hours of exposure to 0.04% or 4% w/v CHG prepared in water, 70% isopropanol, or 70% ethanol at 55°C. CHG solutions prepared with ethanol significantly enhanced heat killing of spores after 1 hour of incubation compared to CHG solutions prepared in either isopropanol or water (P <0.01 compared to isopropanol; P <0.001 compared to water). After 3 hours of incubation in 0.04% w/v CHG, both isopropanol and ethanol enhanced reduction of spores compared to aqueous CHG solution; however, at increased CHG concentrations (4% w/v), spores were completely eliminated by both aqueous and alcoholic preparations. The means of the data from experiments conducted in triplicate are presented. Error bars indicate standard error.