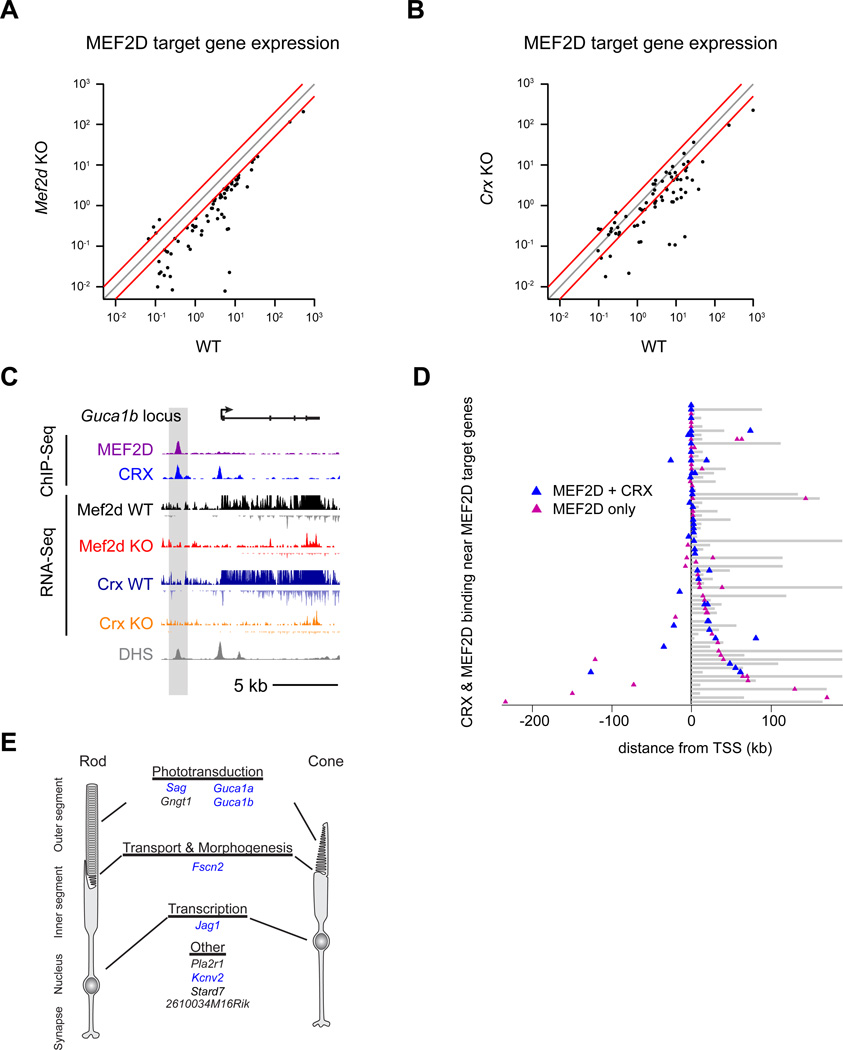
Figure 4. MEF2D and CRX directly co-regulate critical shared target genes.
Average gene expression levels as quantified by exon density of MEF2D direct target genes in WT versus Mef2d KO retinas (A) and WT versus Crx KO retinas (B). N=2 per genotype. Gray line indicates unity. Red lines indicate a two-fold change from unity. (C) UCSC genome browser tracks for MEF2D ChIP-seq and CRX ChIP-seq (Corbo et al., 2010) from WT retinas, as well as for RNA-seq from the retinas of p11 littermate WT and MEF2D KO or WT and CRX KO mice, as well as DNAse hypersensitivity data (ENCODE Consortium) at the Guca1b genomic locus. (D) Distribution of MEF2D binding (magenta triangles) or MEF2D and CRX co-binding (blue triangles) as determined by ChIP-seq with respect to 71 MEF2D target genes. Target gene bodies (gray) are aligned at their transcriptional start sites (TSS, black line). Gene loci are ordered according to the proximity of the nearest MEF2D binding to the TSS. (E) Examples of shared direct MEF2D and CRX target genes relevant to photoreceptor cell biology. Genes implicated in human retinal diseases are in blue.