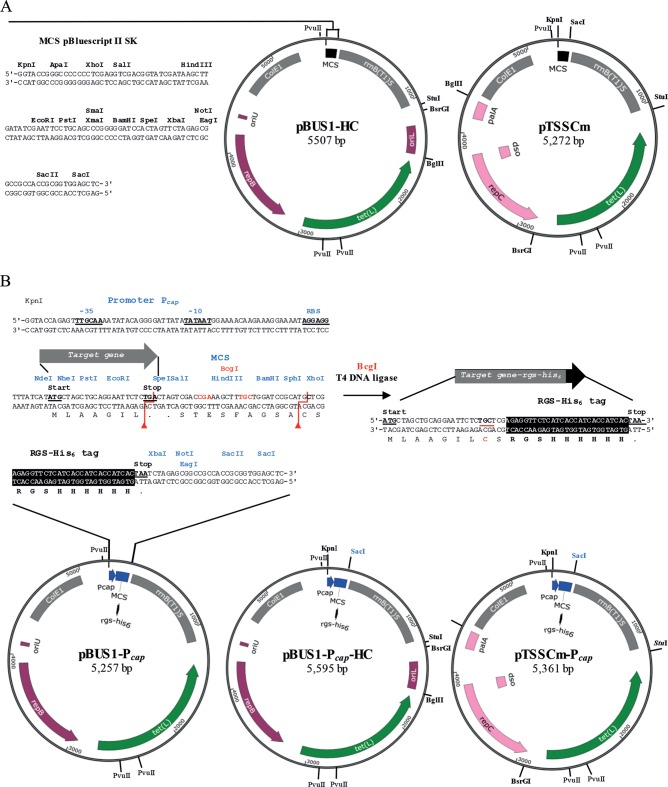
FIG 1.
S. aureus-E. coli shuttle vectors for cloning genes with associated promoters (pBUS1-HC and pTSSCm) and for the constitutive expression of the target gene or the rgs-his6 codon fusion from promoter Pcap (pBUS1-Pcap, pBUS1-Pcap-HC, and pTSSCm-Pcap). The identical backbone segments in all plasmids include the E. coli origin ColE1 and the terminator sequence (rrnB T1)5, shown in gray, and the selectable marker for S. aureus and E. coli tet(L), in green. For propagation in Gram-positive bacteria, the plasmids contain either the pAMα1 replicon shown in violet or the pT181-family replicon in pink. The elements required for rolling-circle replication are indicated: the replication initiator protein gene (repB or repC), the double-strand origin (oriU or dso), and the single-strand origin (oriL or palA). (A) Plasmid maps of pBUS1-HC and pTSSCm containing the multiple cloning site (MCS) derived from pBluescript II SK (Stratagene) as the original pBUS1. (B) Plasmid maps of pBUS1-Pcap, pBUS1-Pcap-HC, and pTSSCm-Pcap containing a novel MCS and the strong promoter (Pcap) and ribosomal-binding site (RBS) of S. aureus type 1 capsule biosynthetic gene 1A. The MCS comprises 15 unique restriction sites and codons for the peptide tag Arg-Gly-Ser-hexa-His (RGS-His6), highlighted in black. The −35, −10 promoter sequences, RBS, and the start and stop codons useful for cloning are indicated in bold and underlined. Recognition and cleavage sites for the enzyme BcgI are indicated in red. Target genes inserted between the NdeI start and the TGA stop codon of the MCS (represented as a gray arrow) can be converted to a target gene-rgs-his6 variant through BcgI digest, followed by ligation. Thereby, the TGA stop codon is mutated to TGC (red underlining), which encodes a cysteine residue. The RGS-His6 tag is linked to the C-terminal end of the protein through two additional amino acids (CS). The plasmid maps were generated using SnapGene software (GSL Biotech, Chicago, IL).