FIG 1.
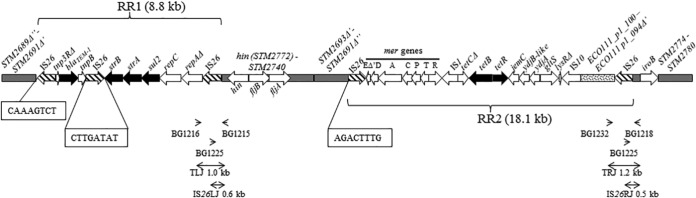
Map of the fljBA operon region of the monophasic variant strain VAR-2009/08643/1 (83,173 bp). IS26 copies are drawn with hatched arrows. Black arrows delineate antibiotic resistance genes. Gray boxes indicate regions homologous to Salmonella Typhimurium LT2 (GenBank accession number AE006468). The dotted box is homologous to a region found on the E. coli plasmid pO111_1 (GenBank accession number AP010961). Antibiotic resistance regions 1 (RR1) and 2 (RR2) are similar to a Salmonella 4,[5],12:i:− chromosomal sequence (GenBank accession number HQ331538) except for (i) a deletion covering partial merE, urf2, and tniAΔ1, (ii) an inverted IS26 element, (iii) a complete IS10 copy, and (iv) an additional region (dotted box) in RR2. Δ′ and Δ″ refer to deletions noticed in the 3′ or 5′ part of some genes, respectively. Boxed nucleotides refer to IS26-associated repeats. The insertion of a 26-kb transposon consisting of the RR1 and RR2 elements occurred at an intermediate stage and was followed by a genomic rearrangement between the first and fourth IS26 copies, leading to an inverted DNA sequence in between. This is supported by the finding of inverted repeats bordering the first and fourth IS elements (boxed nucleotides) and the orientation of the genes within the inverted segment (gray boxes). The arrowheads at the bottom point to primers used to demonstrate the presence of IS26 elements (possibly as part of the 26-kb transposon). Double-headed arrows show the corresponding amplicons with their sizes (TLJ, transposon left junction; IS26LJ, IS26 left junction; TRJ, transposon right junction; IS26RJ, IS26 right junction).
