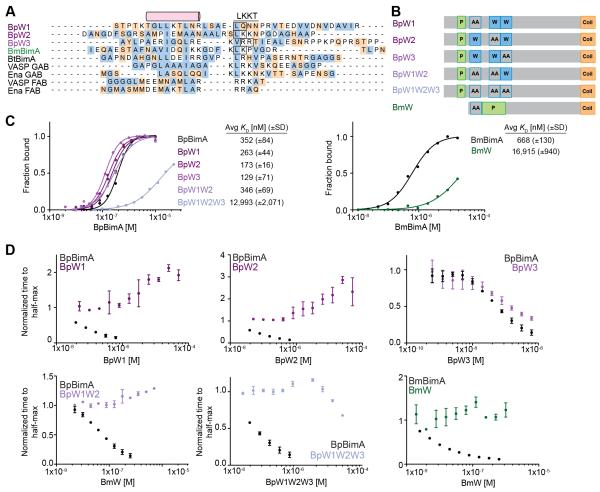
Figure 4. WH2 requirements for BpBimA and BmBimA G-actin binding and nucleation.
(A) Alignment of predicted WH2 sequences from BimA orthologs with known WH2 (GAB and FAB) sequences from human VASP and Drosophila Ena. The conserved α-helix and LKKT motif are indicated. Hydrophobic residues are blue and charged residues orange. Boxed residues were mutated to AA. (B) Domain schematics of WH2 mutant BimA proteins. Predicted WH2 motifs that were mutated are outlined in blue and denoted by AA. (C) Anisotropy measurements of monomeric actin488 binding to BimA. Data are represented by circles, and Hill equation fits are shown as solid lines. The means KD ± SD from at least two experiments are listed. (D) The time to half-maximum fluorescence normalized to actin alone in polymerization reactions with BimA. The means ± SD are shown with wild-type data from Figure 1C for reference.