Figure 2. Hyaluronan metabolism in the allergic lung.
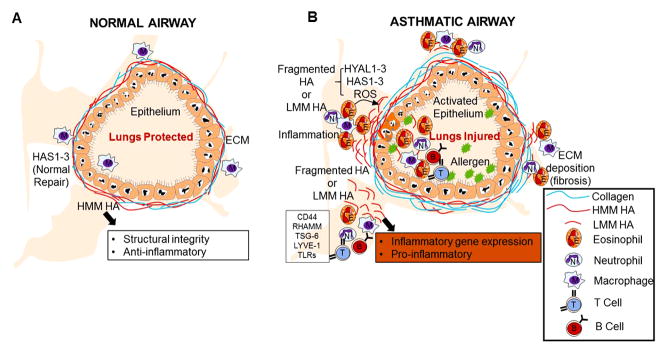
(A) Under physiological conditions high molecular mass HA (HMM HA) protects the lung and helps in the repair process. (B) Under conditions of chronic inflammation or tissue injury hyaluronan synthases (HAS1, HAS2, and HAS3) and hyaluronidases (HYAL1-3) play a role in the generation of fragmented HA (LMM HA). If hyaluronan fragments are generated, the balance shifts from HMM HA to LMM HA. This LMM HA is pro-inflammatory and helps in cellular recruitment and inflammatory gene expression. The differential activities of LMM HA in the lung are regulated through interactions with HA binding proteins including CD44, RHAMM, TSG-6, LYVE-1, and TLRs. Altering the balance of LMM HA and HMM HA may have therapeutic utility in the treatment of lung inflammation.
