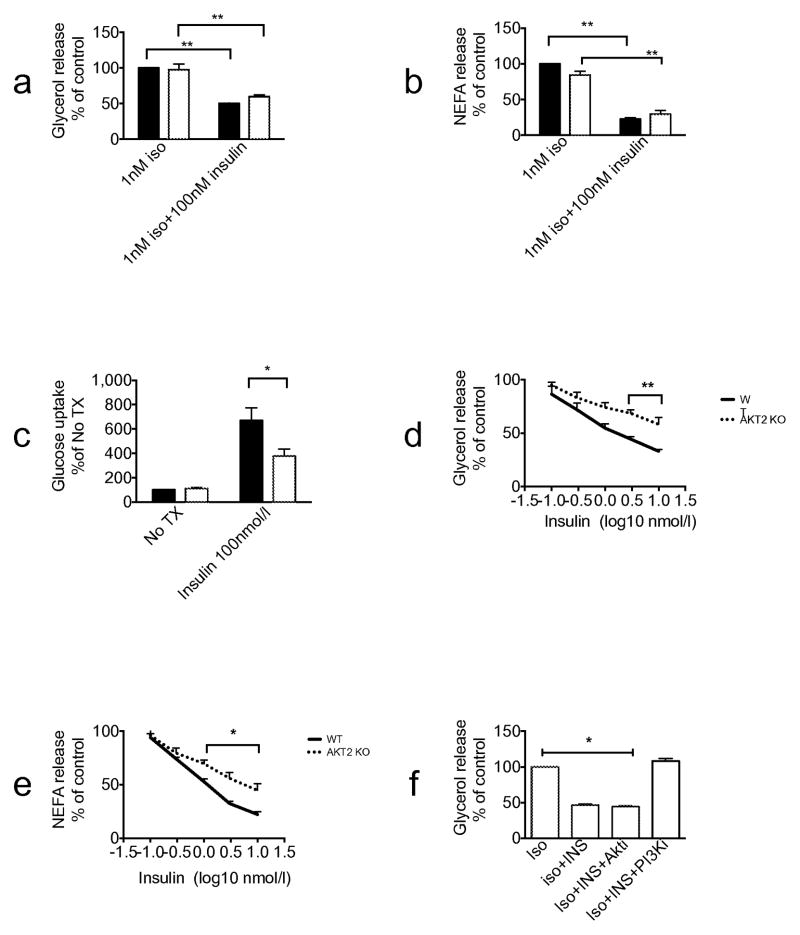
Fig. 6.
Insulin inhibits isoprenaline-induced lipolysis in primary brown adipocytes of Akt2 null mice. Primary brown adipocytes were isolated from either wild-type or Akt2 null pups. The cells were treated with 1 nmol/l isoprenaline (Iso) ± 100 nmol/l insulin (INS). (a) Glycerol release assay and (b) NEFA release assay were performed. Data are presented as % of maximal response of wild-type cells to 1 nmol/l isoprenaline. (c) 2-Deoxyglucose uptake assay was performed with no treatment and with 100 nmol/l insulin. Insulin dose-response curves of (d) glycerol and (e) NEFA release were generated using 1 nmol/l isoprenaline stimulation. (f) Glycerol release assay in the presence of 1 nmol/l isoprenaline ± 100 nmol/l insulin ± 20 μmol/l AktiVIII (Akti) ±10 μmol/l PI-103 (PI3Ki). Data are expressed as means ± SEM from 2–4 experiments. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, as indicated. No Tx, no treatment, WT, wild-type