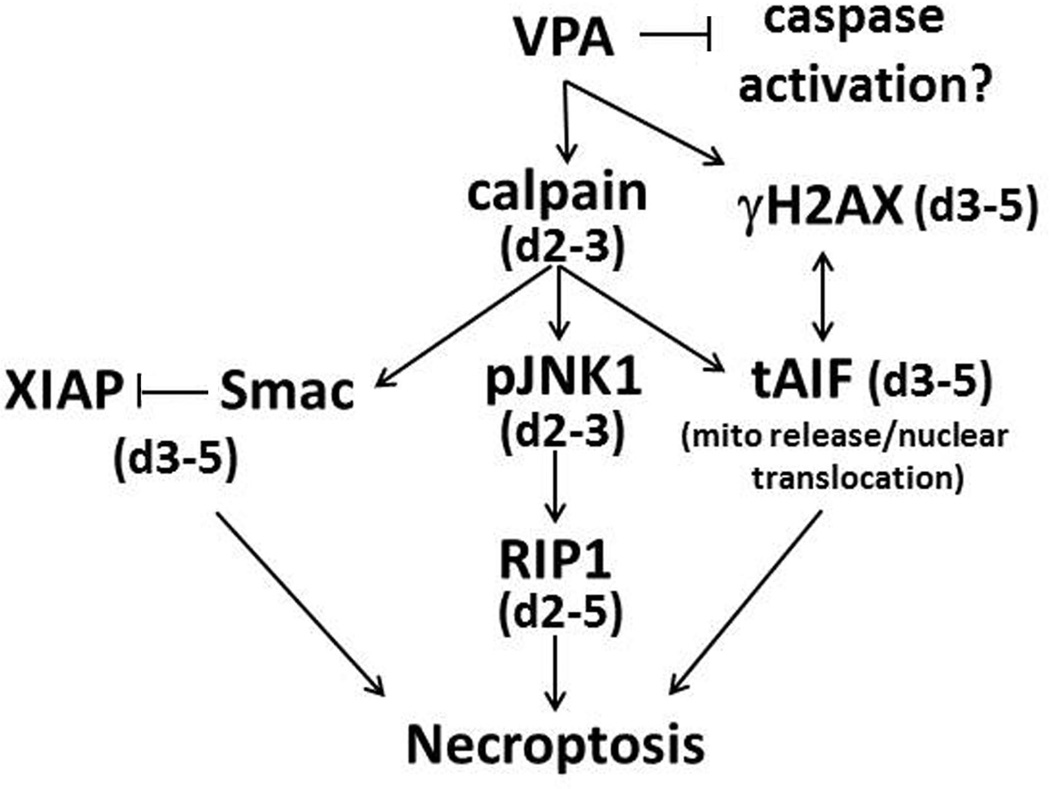
Figure 7. Schematic representation of VPA-induced neuronal cell death.
Our data confirm a VPA-induced necroptotic pathway that initiates with calpain activation and is accompanied by calpain-dependent activation of JNK1, which is responsible for increased RIP-1 expression. Calpain induces Smac/DIABLO expression as well as cleavage and nuclear translocation of AIF. VPA increases nuclear H2AX, which can complex with tAIF to promote chromatinolysis and necroptotic cell death. Smac/DIABLO increase is accompanied by reduced expression of XIAP, further contributing to necroptosis. These pathways are not activated in PC47 cells that have constitutively activated survival pathways. D= days post-VPA-treatment.