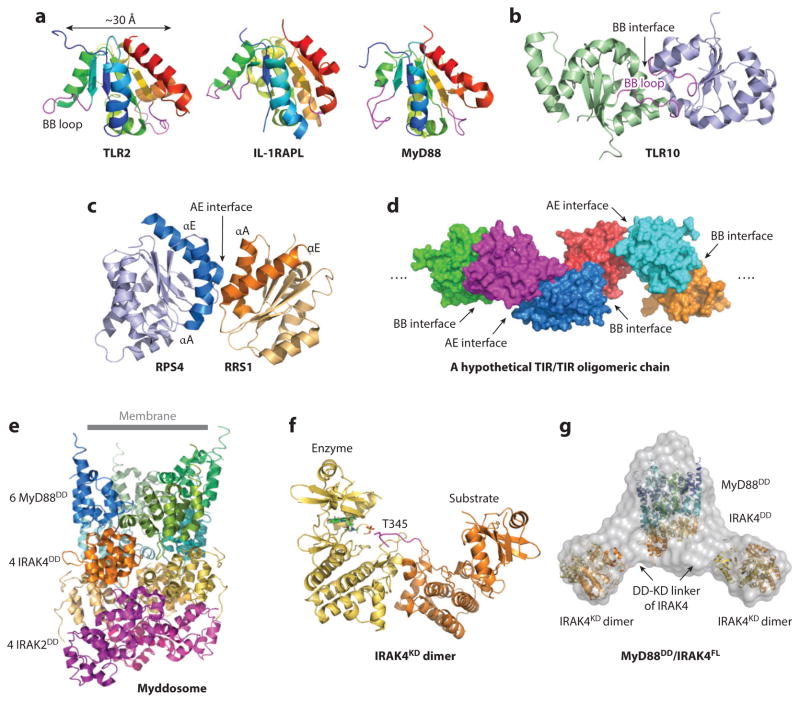
Figure 3.
The TLR/IL-1R superfamily: intracellular signaling. (a) Cartoon representations of TIR domain structures. TIR domains of TLR2, IL-1RAPL, and MyD88 are aligned to the same orientation. Location of the BB loop is indicated. (b) Arrangement of TLR10 TIR homodimer structure using the BB interface. (c) Structure of the RPS4/RRS1 TIR domain heterodimer formed using the AE interface. The location of the dimerization interface is indicated. (d) Model of a hypothetical TIR/TIR oligomerization chain, based on iterative BB and AE interfaces. (e) Representation of the Myddosome DD complex structure. (f) Structure of the inactive IRAK4 KD dimer. (g) The SAXS/WAXS envelope of the MyD88DD/IRAK4FL complex fitted with one binary Myddosome DD complex and two IRAK4 KD dimers. Abbreviations: DD, death domain; FL, full length; IL-1RAPL, interleukin-1 receptor accessory protein-like; IRAK, IL-1R-associated kinase; KD, kinase domain; RPS, resistance to Pseudomonas syringae; RRS, resistance to Ralstonia solanacearum; TIR, Toll-IL-1R; TLR, Toll-like receptor.