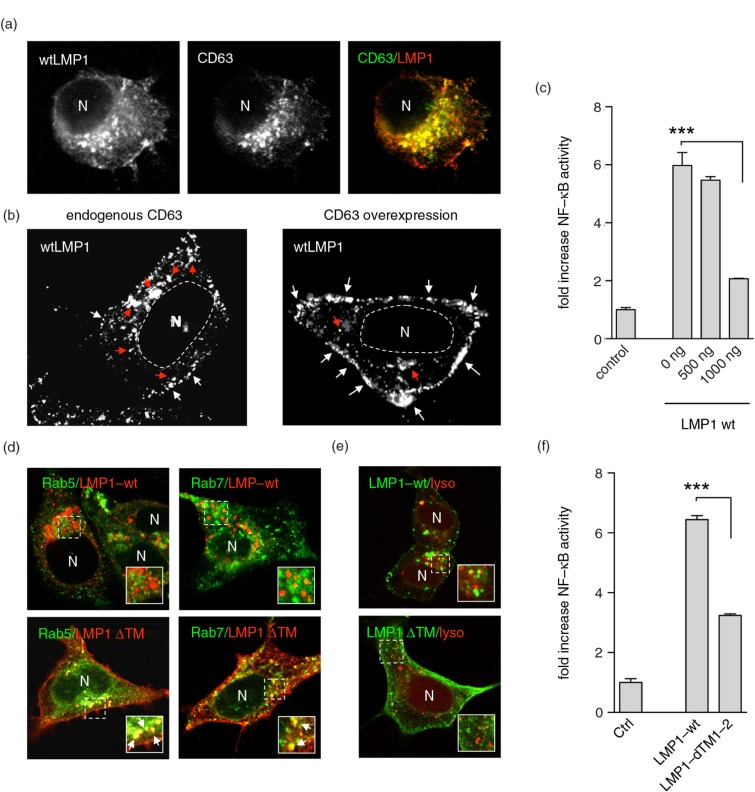
Fig. 1.
LMP1 accumulates at and signals from CD63+ endosomes. (a) Immunofluorescent labelling of wtLMP1 (red) and CD63 (green) in HEK293 cells. (b) Immunofluorescent labelling of wtLMP1 in HEK293 cells with endogenous CD63 levels or overexpression of CD63. White and red arrowheads indicate LMP1 localized at the plasma membrane or endosomal membranes, respectively, and N indicates nucleus. (c) Reporter assay for effect of CD63 on LMP1-wt NFκB activity. Cell lysates of HEK293 cells transfected for 24 hours with wtLMP1 (LMP1-WT) and increasing amounts of CD63 plasmid or empty vector (control), together with an NFκB–reporter construct. Error bars represent s.d.; shown is one representative experiment; n=3. (d) Immunofluorescent labelling of LMP1-wt or LMP1ΔTM1-2 (LMP1 ΔTM) (both in red) in HEK293 cells co-transfected with Rab5- or Rab7-GFP (both in green). N indicates nucleus. (e) Immunofluorescent labelling of Lysotracker (red) in LMP1-wt or LMP1 ΔTM (green) transfected HEK293 cells. N indicates nucleus. (f) Reporter assay for LMP1-wt or LMP1-ΔTM1-2 NFκB activity. Cell lysates of HEK293 cells transfected with wtLMP1 (LMP1-WT), LMP1-ΔTM1-2 (LMP1-ΔTM1-2), or empty vector (control), together with an NFκB–reporter construct. Error bars represent s.d.; shown is one representative experiment; n=3.