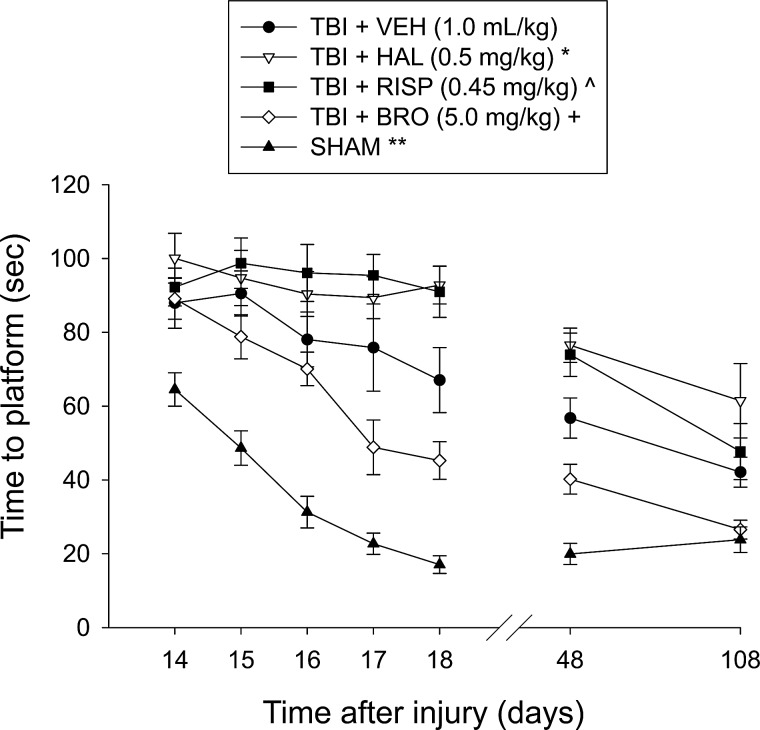
FIG. 3.
Mean (±SEM.) time (sec) to locate a hidden (submerged) platform in a water maze. During postoperative days 14–18, all TBI groups were significantly impaired versus SHAM controls. Moreover, the TBI+HAL and TBI+RISP groups were significantly impaired versus the TBI+VEH group, though they were not different from one another. In contrast, the TBI+BRO group located the escape platform significantly quicker over time, compared to all other TBI groups. These effects persisted at 1 month after drug withdrawal (i.e., day 48). At 3 months after drug withdrawal (i.e., day 108), TBI+HAL rats continued to perform worse than the TBI+VEH group, whereas the TBI+RISP group displayed some improvement and was not significantly different from VEH-treated rats. The TBI+BRO group remained significantly better than all TBI groups. *p<0.005 versus TBI+vehicle and TBI+BRO on days 14–18, 48, and 108; ^p<0.005 versus TBI+vehicle and TBI+BRO on days 14–18 and 48, but only from TBI+BRO on day 108; +p<0.005 versus all TBI groups at each time point; **p<0.0001 versus all TBI groups at each time point, except TBI+BRO on day 108. TBI, traumatic brain injury; VEH, vehicle; HAL, haloperidol; RISP, risperidone; BRO, bromocriptine.