Fig 4.
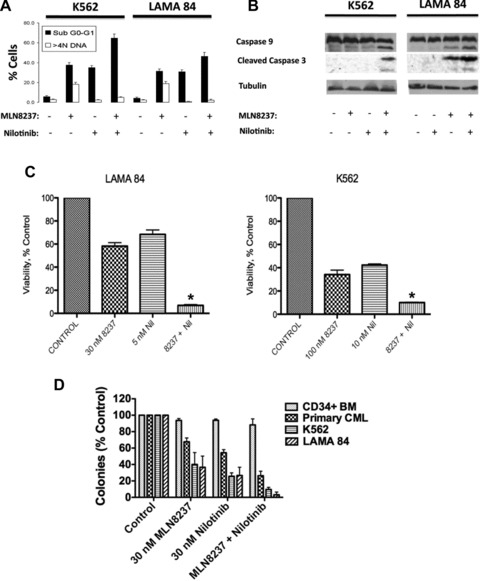
MLN8237 significantly increases the efficacy of nilotinib. (A) MLN8237 potentiates the pro-apoptotic effects of nilotinib. LAMA 84 and K562 cells were treated with 30 nM MLN8237, 10 nM nilotinib or the combination for 48 hrs. Percentages of cells with sub-G0-G1 DNA were determined by PI/FACS. n= 3 ± S.D. (B) The combination of MLN8237 and nilotinib induces mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis. K562 and LAMA 84 cells were treated with 100 nM MLN8237, 30 nM nilotinib or both for 24 hrs. Protein lysates were subjected to SDS-PAGE, blotted, and probed with active caspase-3 and caspase-9 antibodies. Anti β-tubulin was used as a loading control. (C) Co-treatment with MLN8237 and nilotinib results in significantly greater growth inhibition and reduction in survival than that achieved by either agent alone. Cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of MLN8237 for 96 hrs and viability was assessed by MTT assay. Error bars indicate the S.D. *P < 0.05. (D) Effects of MLN8237 and nilotinib on clonogenic survival. CD34+ normal bone marrow (n= 3), primary CML from patients in blast crisis (n= 3), K562 and LAMA 84 cells were treated with MLN8237, nilotinib or both drugs for 24 hrs. Cells were plated and scored as described in the ‘Materials and methods’.
