Fig 6.
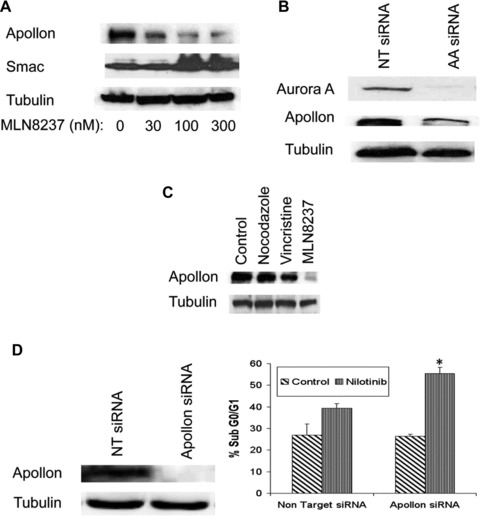
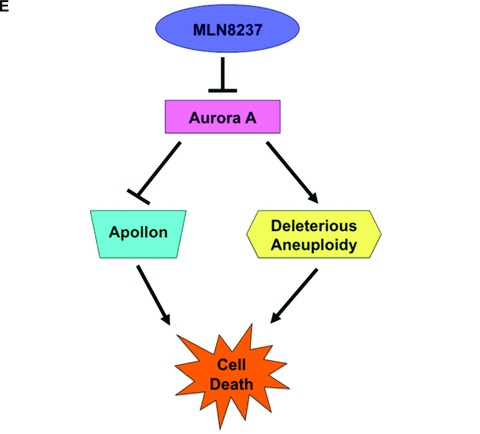
Targeting Apollon expression sensitizes CML cells to nilotinib-induced apoptosis. (A) MLN8237 treatment results in a dose-dependent reduction in the large IAP, Apollon and increased expression of its substrate, Smac. LAMA 84 cells were treated with MLN8237 for 24 hrs. Protein lysates were subjected to SDS-PAGE, blotted, and probed with Apollon and Smac antibodies. Tubulin documented equal loading. (B) Aurora A SMARTpool or siCONTROL siRNA directed at luciferase were transfected into LAMA 84 cells using the Nucleofector II. (C) General disruption of mitosis does not significantly affect Apollon expression. LAMA 84 cells were treated with nocodazole, vincristine or MLN8237 for 24 hrs. Protein lysates were subjected to SDS-PAGE, blotted, and probed with an Apollon antibody. Tubulin documented equal loading. (D) Apollon SMARTpool or siCONTROL siRNA directed at luciferase were transfected into LAMA 84 cells using the Nucleofector II. Tubulin was used as a loading control. LAMA 84 cells transfected with Apollon-targeted siRNA and non-targeted siRNA were treated with nilotinib for 48 hrs and the percentage of apoptotic cells were determined by PI/FACS analysis. n= 3 ± S.D., *P < 0.05. (E) Schematic depicting the multiple anti-leukaemia properties of the MLN8237. MLN8237 inhibits Aurora A kinase leading to deleterious aneuploidy, inhibition of the IAP, Apollon and cell death.
