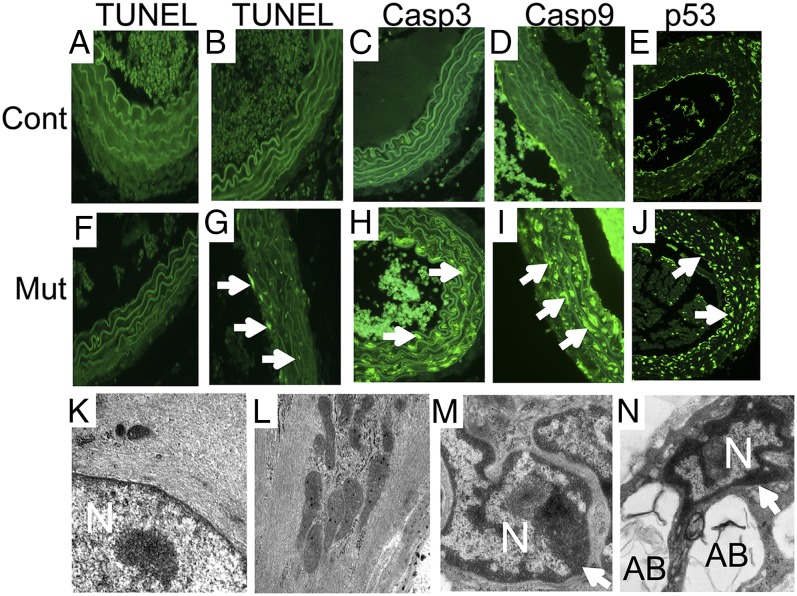
Fig. 5.
Late-stage induction of apoptosis in myocardin-deficient aortic SMCs. At 14 d (A and F) and 4 mo (B–E and G–J) following tamoxifen treatment, the aorta isolated from MyocdF/F (Cont) and SMMHC-CreERT2/MyocdF/F (Mut) mice were fixed, sectioned, and TUNEL-stained or immunostained to survey apoptosis. (A, B, F, and G) Representative photomicrographs demonstrate only rare TUNEL-positive nuclei (green) in the control (A) or conditional mutant (F) aorta 14 d following tamoxifen treatment. By contrast, 4 mo following tamoxifen exposure, widespread TUNEL-positive nuclei (arrows) are observed in the SMMHC-CreERT2/MyocdF/F mutant aorta (G) but not in the control (B). In addition, activated caspase 3 (arrow, green stain), caspase 9 (arrow, green stain), and p53 (arrows) are observed in medial SMCs populating the aorta of tamoxifen-treated SMMHC-CreERT2/MyocdF/F mutant mice (H–J) but not in control mice (C–E). Original magnification, 400×. (K–N) EM of aortic sections prepared from tamoxifen-treated MyocdF/F control (K and L) and SMMHC-CreERT2/MyocdF/F mutant (M and N) mice reveals preserved nuclear (N) architecture with dispersed chromatin and abundant myofibers in vascular SMCs (K and L). By contrast, nuclear chromatin condensation (arrows), nuclear fragmentation, and cytoplasmic apoptotic body (AB) formation are observed in SMCs populating the aorta of SMMHC-CreERT2/MyocdF/F mutant mice (M and N). Original magnification, 50,000×.