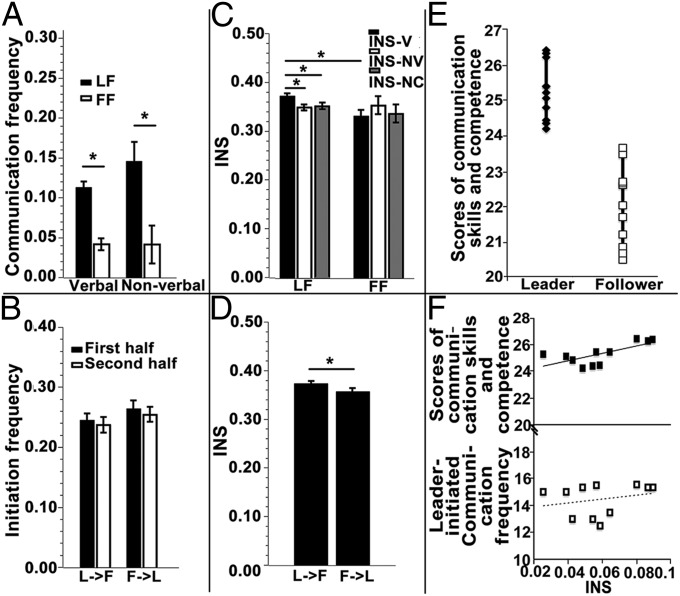
Fig. 2.
(A) Verbal and nonverbal communication frequencies during the task. The averaged frequency of the two leader–follower (LF) pairs (black) was higher than the frequency of the follower–follower (FF) pairs (white). (B) There were no significant differences in leader-initiated (L→F) vs. follower-initiated (F→L) verbal communications. (C) LF pairs’ INS during verbal communication (INS-V) was higher than INS for all other situations. NC, no communication occurred; NV, nonverbal communication; V, verbal communication. (D) INS during leader-initiated communication was higher than that during follower-initiated communication. (E) Leaders’ communication skills and competence were more highly rated than those of the followers. (F) INS during leader-initiated communication was positively associated with ratings of communication skills and competence (Upper), but not with leader-initiated communication frequency (Lower). *P < 0.05.