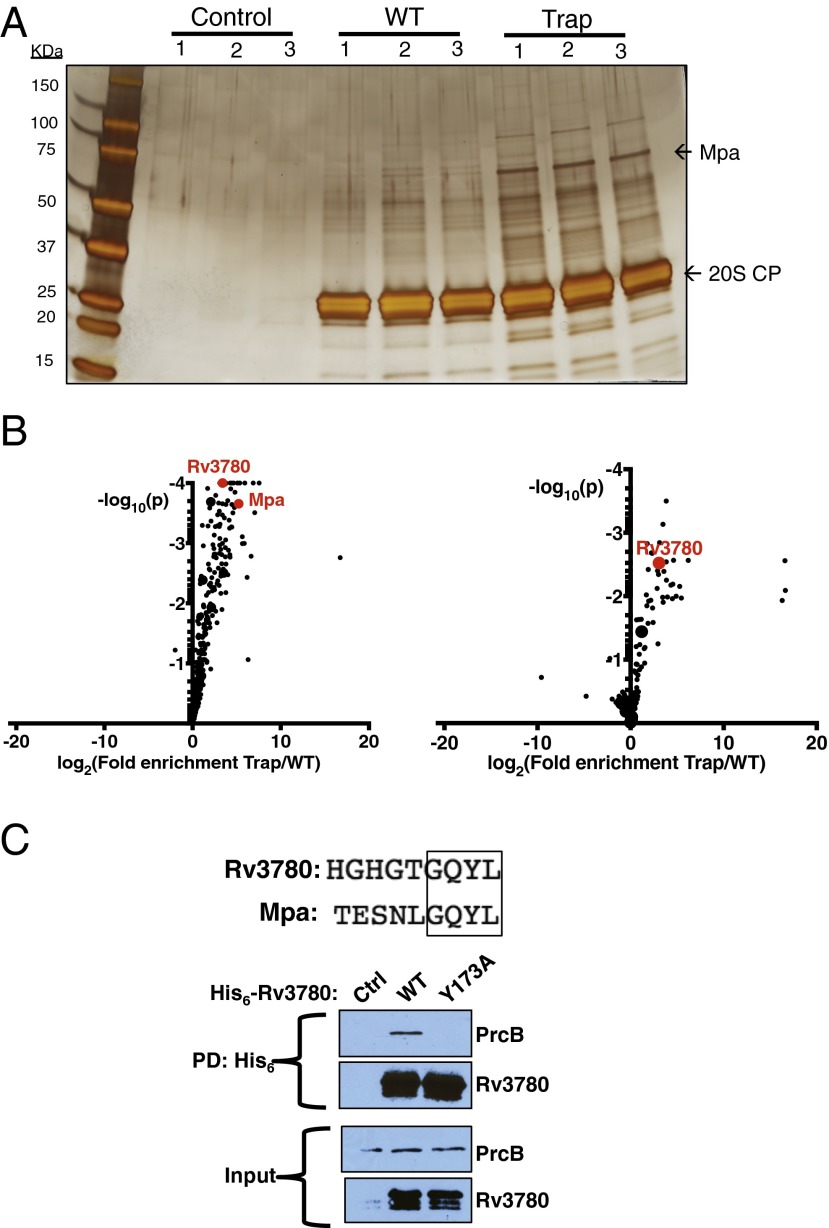
Fig. 1.
Rv3780 interacts with the M. tuberculosis proteasome. (A) A proteasome trap identifies interacting proteins. A TAP-tagged active (WT) or catalytically inactive (Trap) 20S CP was overproduced in M. tuberculosis and isolated from lysates by Ni-NTA and anti-FLAG affinity purification. Proteins were separated by 12% (wt/vol) SDS/PAGE and visualized by silver staining. Molecular mass markers in kDa. (B) Proteins that were enriched in pull-downs using the proteasome trap. The eluates generated in A were modified by TMT labeling and their relative levels were quantified by MS. The log2 ratio of relative abundance in the Trap pull-down vs. the WT pull-down from WT M. tuberculosis (Left) or an mpa mutant (Right) is plotted against the log10 p-value as determined by t test using three biological replicates. Data points representing the top 10 copurified proteins of highest abundance with the Trap are enlarged. Data points representing Mpa and Rv3780 are in red. (C) Rv3780 requires a conserved penultimate Tyr to copurify with 20S CPs. His6-tagged WT or Y173A Rv3780 was overproduced in M. tuberculosis and isolated from lysates by Ni-NTA affinity purification. Proteins were visualized by immunoblotting for PrcB or Rv3780 using antibodies raised against PrcB–His6 or Rv3780–His6, respectively. PD, pull-down.