Fig. 7.
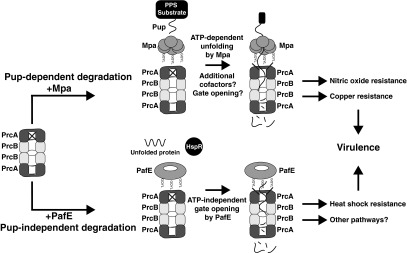
Model of two independent pathways of proteasomal degradation in M. tuberculosis. For Pup-dependent degradation, a substrate protein must first be modified by Pup, which binds to Mpa. Mpa then unfolds the pupylated protein in an ATP-dependent manner, and the 20S CP degrades the unfolded protein. For Pup-independent degradation, substrates are likely to be small, unfolded, or easily misfolded proteins such as HspR. These substrates are degraded by the proteasome upon gate opening, which is induced by PafE.
