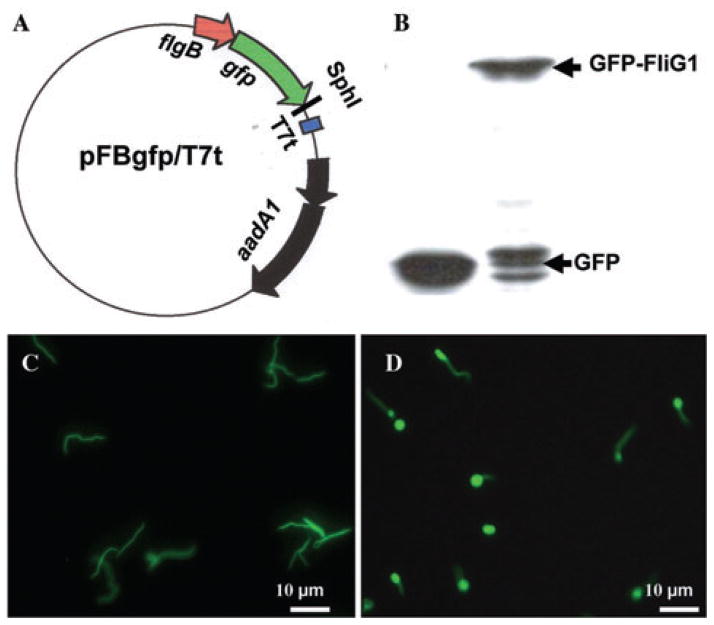
Fig. 6. Localization of FliG1 in B. burgdorferi.
A. Constructing a vector that expresses the N-terminal GFP-fusion proteins. The flgB promoter element was fused to gfp with a five-glycine linker, and SphI cloning site was engineered at the 3′ end of gfp. A target gene, such as fliG1, will be fused to gfp at the SphI site. A T7 transcription terminator was inserted.
B. Detection of GFP–FliG1 fusion protein using Western blot. A monoclonal antibody against GFP (Invitrogen) was used to detect GFP and GFP–FliG1. GFP is about 27 kDa and GFP–FliG1 is about 75 kDa.
C. The fluorescence micrograph (40×) of the fliG1 mutant that was transformed with the plasmid pFBgfp/T7t, which only expresses GFP.
D. The fluorescence micrograph (40×) of the fliG1 mutant that was transformed with the plasmid pFBgfp–fliG1/T7t, which expresses GFP–FliG1 fusion protein. The brighter ends represent the location of GFP–FliG1.