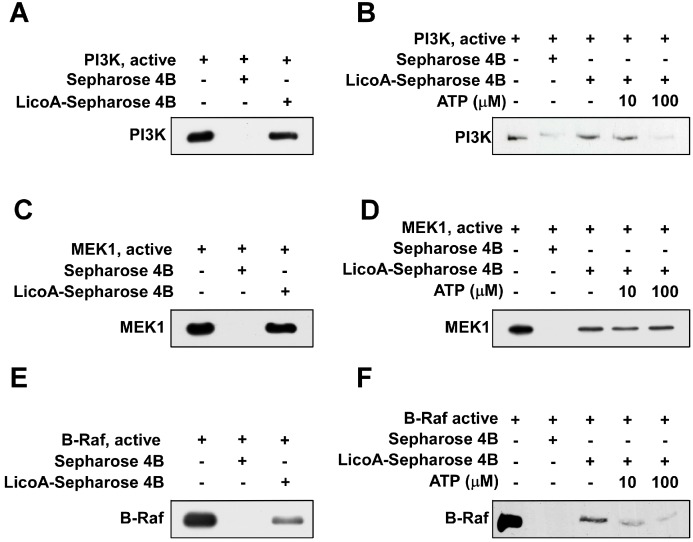
Figure 4.
LicoA directly binds with PI3K, MEK1, and B-Raf. (A, C and E) LicoA specifically binds with PI3K (A), MEK1 (C), and B-Raf (E) in vitro. The PI3K (or MEK1, B-Raf)—LicoA binding was confirmed by immunoblotting using antibodies against PI3K(p110), MEK1 or B-Raf: Lane 1 (input control), PI3K, MEK1, or B-Raf protein standard; Lane 2 (control), Sepharose 4B was used to immunoprecipitate PI3K, MEK1, or B-Raf, as described in the Experimental Section; Lane 3, LicoA-Sepharose 4B affinity beads were used to immunoprecipitate PI3K, MEK1, or B-Raf. (B, D and F) LicoA competes with ATP to bind with PI3K and B-Raf but not MEK1. Active PI3K, MEK1, or B-Raf (200 ng) was incubated with ATP at different concentrations (0, 10, or 100 µM) and 100 µL of LicoA-Sepharose 4B or 100 µL of Sepharose 4B (negative control) in reaction buffer for a final volume of 500 µL. The mixtures were incubated at 4 °C overnight with shaking. After washing, the immunoprecipitated proteins were detected by Western blotting: Lane 1 (input control), PI3K, MEK1, or B-Raf protein standard; Lane 2 (negative control), PI3K, MEK1, or B-Raf bound with Sepharose 4B; Lane 3 (positive control), PI3K, MEK1, or B-Raf binding with LicoA—Sepharose 4B. Each experiment was performed a minimum of three times and representative blots are shown.