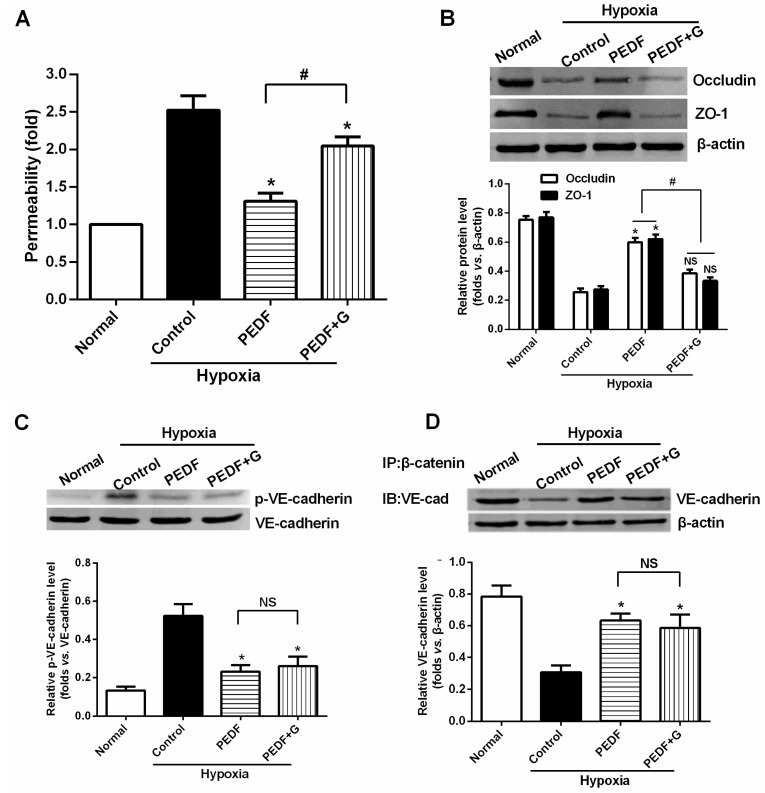
Figure 6.
PEDF inhibits hypoxia-induced RAEC permeability through PPARγ-dependent tight junction (TJ) production. (A) Endothelial permeability determination. PEDF’s effect on the suppression of the endothelial permeability was significantly lost in the presence of PPARγ inhibitor GW9662. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD (n = 6). * p < 0.05 vs. the control group, # p > 0.05; (B) Western blot determination of TJs (occludin and ZO-1). * p < 0.05 vs. the control group, # p < 0.05; NS, p > 0.05 vs. the control group (n = 3); (C) Western blot determination of VE-cadherin/VE-cadherin tyrosine phosphorylation. * p < 0.05 vs. the control group; NS, p > 0.05 (n = 3); and (D) Co-immunoprecipitation of VE-cadherin/β-catenin complexes. * p < 0.05 vs. the control group; NS, No statistical difference (n = 3). These findings suggest that PEDF inhibits RAEC permeability under hypoxia via enhancing the expression of TJs and adherens junctions (AJs). PEDF inhibits hypoxia-induced RAECs permeability through PPARγ-dependent TJ production (n = 3).