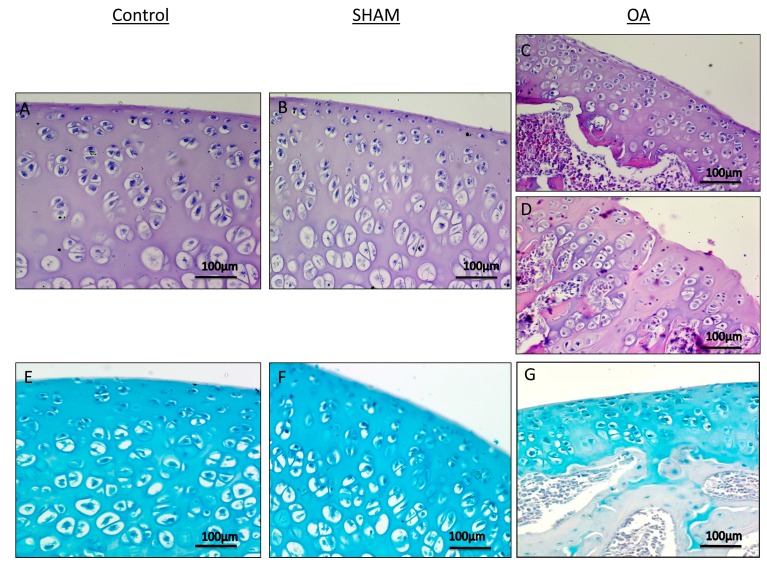
Figure 2.
Histological and histochemical evaluation. (A,B) Histology (H&E staining) demonstrated the absence of structural alterations in control groups ((without anterior cruciate ligament transection (ACLT)). In the superficial zone, cells appear flat and small; in the middle and deep zone, cells are organized in columns. Magnification ×20; Scale bars: 100 µm; (C) Histology (H&E staining) demonstrated evidence of structural alterations in cartilage with moderate signs of OA (with ACLT). The structural alterations included a reduction of cartilage thickness in the superficial and the middle zones. The tidemark is no longer intact and the subchondral bone shows fibrillation. Magnification ×20; Scale bars: 100 µm; (D) Histology (H&E staining) demonstrated signs of structural alterations in severe Osteoarthritis (OA) (with ACLT). Severe OA cartilage shows deep surface clefts, disappearance of cells from the superficial zone, cloning, and a lack of cells in the intermediate and deep zone, which are not arranged in columns. The cartilage layers (superficial zone, middle and deep zone) are completely absent. Magnification ×20; Scale bars: 100 µm; (E,F) Histochemistry (toluidine blue staining) showed an absence of structural alterations and preserved GAG, in control groups (without ACLT), as indicated by the intense toluidine blue staining. Magnification ×20; Scale bars: 100 µm; (G) Histochemistry (toluidine blue staining) demonstrated signs of structural alterations in moderate and severe OA cartilage and loss of proteoglycans as evidenced by poor GAG preservation in the OA group (with ACLT), showing reduced toluidine blue staining. Magnification ×20; Scale bars: 100 µm.