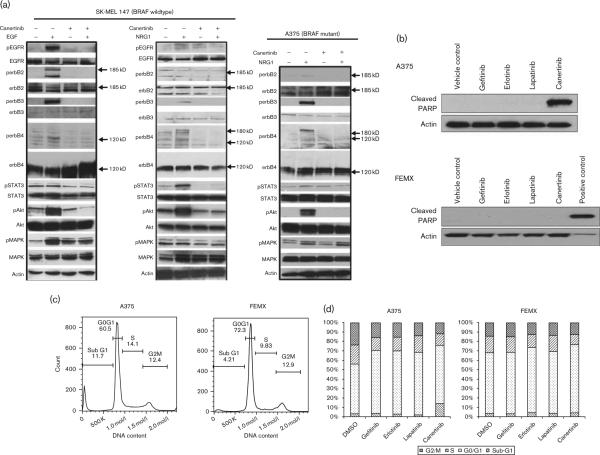
Fig. 3.
Canertinib inhibits ligand-induced coactivation between different erbB receptors and downstream Akt signaling and induces apoptosis and sub-G1 arrest in melanoma cells. (a) SK-MEL147 (BRAF WT) and A375 (BRAF mutant) cells were serum deprived for 48 h. Cells were pretreated with canertinib (5 μmol/l) for 1 h before stimulation with EGF (20 nmol/l) or NRG1 (20 nmol/l) for 15 min. Representative western blots are shown from three individual experiments. (b) A375 BRAF mutant cells or FEMX WT cells were treated for 16 h with gefitinib, erlotinib, lapatinib, or canertinib at 10 μmol/l. Cell lysates were prepared and analyzed for cleaved PARP expression by western analysis. β-Actin was used as a control. Representative western blots are shown from three individual experiments. (c) Representative histogram of cell cycle analysis in A375 and FEMX cells following treatment with 10 μmol/l canertinib for 16 h. The percentage of cells in each phase is shown. (d) Quantitative representation of cell cycle analysis in A375 and FEMX treated with gefitinib, erlotinib, lapatinib, or canertinib. Data are the mean of two independent experiments each of which had three samples per treatment. DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide; EGF, epidermal growth factor; NRG, neuregulin; WT, wildtype.