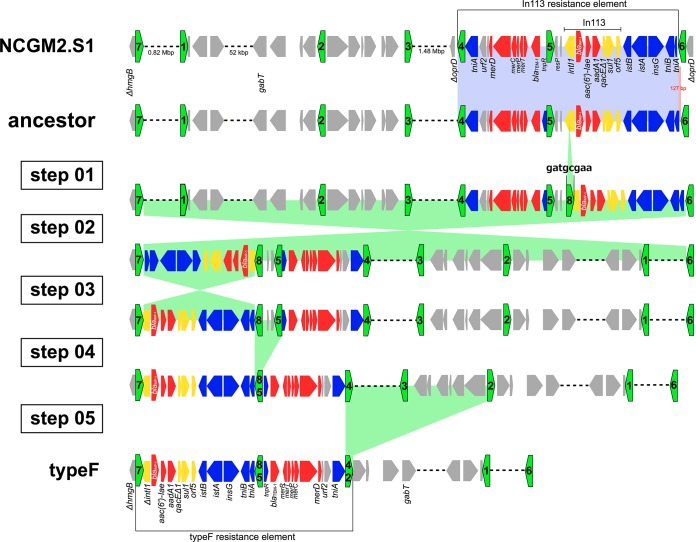
FIG 5.
Hypothetical model of the genesis of P. aeruginosa PA058447 carrying the type F resistance element from an ancestor P. aeruginosa strain carrying the In113 resistance element. Green pentagons indicate IS26s and their orientations. Color shading indicates homologous regions. Coding sequences are shown as pentagons (green, IS26; blue, transposon; yellow, integron; red, antibiotic resistance gene; gray, other function or hypothetical protein). The In113 resistance element in an ancestor P. aeruginosa isolate is an IS26-transposon. The IS26 transposon can be translocated into oprD to create NCGM2.S1. Genesis of P. aeruginosa PA058447 carrying the type F resistance element from the ancestor P. aeruginosa strain carrying the In113 resistance element can be achieved through IS26-8 insertion into intl1 (step 01), genomic inversions (steps 02 and 03), and genomic deletions (steps 04 and 05) (the numbering of the steps does not imply a particular order).