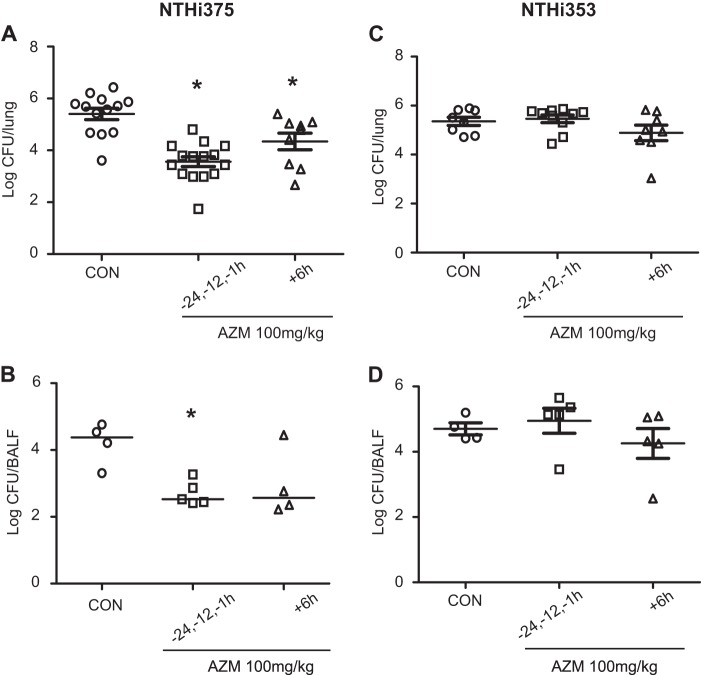
FIG 4.
Effect of AZM administration on bacterial loads in CD1 mice infected by NTHI. Mice were infected intranasally with ∼108 bacteria/mouse. AZM (100 mg/kg/dose) was administered orally. Controls were as follows: animals were administered vehicle solution but did not receive AZM. Bacterial counts were determined at 12 hpi for lungs (log10 CFU/lung) (A and C) and BALF (log10 CFU/BALF sample) (B and D). (A) Impact of AZM on NTHI 375 counts in lungs. NTHI 375 counts were significantly lower in mice treated with AZM prior to (1, 12, and 24 h before infection) and/or after (6 hpi) infection than in control (CON) mice (P < 0.0001 and P < 0.05, respectively). (B) Effect of AZM on NTHI 375 bacterial counts in BALF samples. NTHI 375 counts were significantly (P < 0.005) lower in mice treated with AZM prior to infection than in control mice. (C and D) Impacts of AZM use on NTHI 353 bacterial counts in lungs (C) and BALF (D). NTHI 353 counts were similar for all mouse groups.