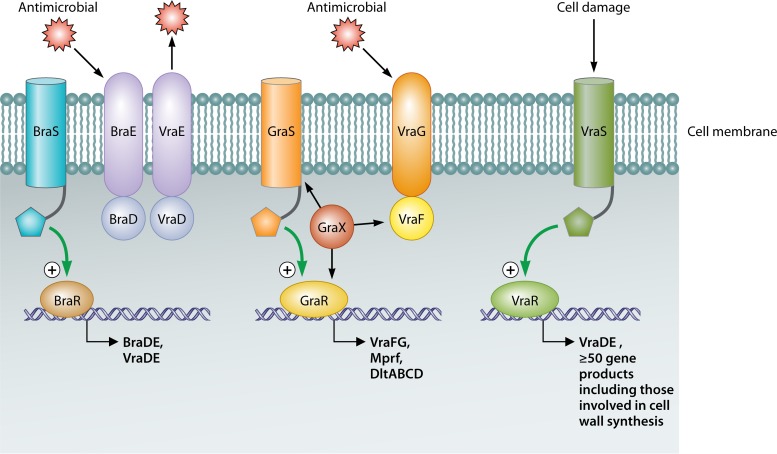
FIG 3.
In S. aureus, three main TCSs are responsible for lantibiotic/antimicrobial resistance. These include two Bce-like TCSs, BraRS and GraRS, and an Lia-like TCS, VraSR. A coordinated resistance effort results from the actions of these TCSs, causing upregulation of genes whose products alter the composition of the cell wall and membrane and also of genes encoding ABC transporters which expel antimicrobials from the cell.