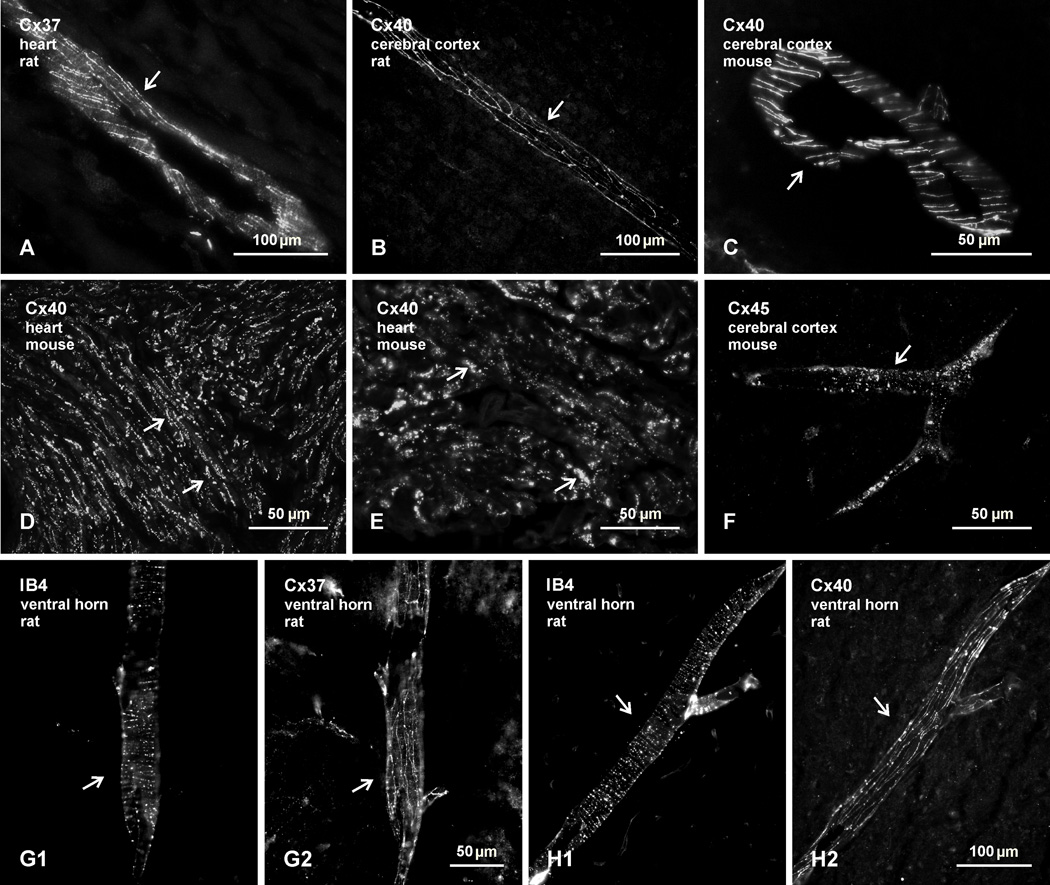
Fig. 1.
Confirmation of immunofluorescence labelling with anti-connexin antibodies in various tissues of adult rat and mouse. (A–C) Immunolabelling for Cx37 in rat heart (A), and Cx40 in rat (B) and mouse (C) cerebral cortex, showing detection of linear arrangements of these connexins along blood vessels (arrows), in accordance with patterns of their organization and localization at gap junctions between endothelial cells. (D,E) Labelling for Cx40 at low (D) and higher (E) magnification in atrium of mouse heart, where Cx40 is concentrated in gap junctions between lateral membranes of cardiomyocytes (D, arrows) and in gap junctions at intercalated discs (E, arrows). (F) Labelling of Cx45 along a blood vessel in mouse cerebral cortex (arrow), reflecting association of Cx45-puncta with vascular smooth muscle cells. (G,H) Images showing blood vessels in the spinal cord ventral horn labelled for the vessel marker IB4 (G1,H1, arrows) and images of the same vessels labelled for either Cx37 (G2, arrow) or Cx40 (H2, arrow), respectively, confirming vascular localization of the two connexins in spinal cord.